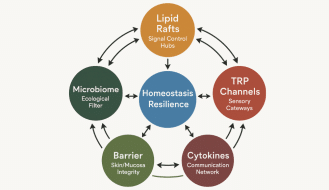
The Relationship Between Vitamin D and Skin Health
Vitamin D, often called the “Sunshine Vitamin,” is essential for many aspects of health, but one of its most overlooked benefits is its role in skin health. While we often associate vitamin D with bone health and immune function, this powerful nutrient also plays a major role in maintaining healthy, resilient skin.
Our bodies naturally produce vitamin D when exposed to sunlight, but deficiency is incredibly common. In fact, an estimated 35% of American adults — and nearly 1 billion people worldwide — are vitamin D deficient (1). Low levels of vitamin D have been linked to a range of skin issues, from dryness and irritation to inflammatory conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
 Because vitamin D helps reduce inflammation, regulate oil production, and promote skin cell turnover, people with adequate vitamin D levels often notice clearer, smoother, and more even-toned skin.
Because vitamin D helps reduce inflammation, regulate oil production, and promote skin cell turnover, people with adequate vitamin D levels often notice clearer, smoother, and more even-toned skin.
How Vitamin D Benefits Skin Health
Vitamin D3, the active form of vitamin D produced in the skin with the help of UV rays, plays a crucial role in keeping your skin strong, resilient, and healthy. While too much sun exposure can lead to premature aging and damage, getting the right amount is essential for producing this vital nutrient.
Vitamin D3 works at the cellular level to repair skin damage, regulate the immune system, and prevent premature aging (2). When your skin has enough vitamin D, it’s better equipped to protect itself from inflammation, dryness, and environmental stressors.
Here’s how vitamin D3 supports healthy skin:
- Strengthens the Skin Barrier: Your skin barrier is like a shield, keeping moisture in and harmful irritants out. Vitamin D3 helps reinforce this barrier, reducing the risk of dryness, irritation, and infections.
- Regulates the Immune System: Vitamin D helps control the skin’s immune response (3), reducing skin inflammation and fighting off harmful bacteria that can lead to conditions like acne and eczema.
- Slows Down Skin Aging: By promoting healthy skin cell turnover and protecting against oxidative stress, vitamin D3 can help slow signs of aging (4) like fine lines and wrinkles.
- Repairs UV Damage: While excessive UV exposure can harm the skin, vitamin D3 plays a role in repairing damage caused by the sun and supporting overall skin renewal.
Impact of Vitamin D Deficiency on Skin Cells
When levels are low, the skin’s ability to function properly is compromised, leading to a range of issues that affect both appearance and overall skin health.
One of the key roles of vitamin D in the skin is helping skin cells grow, develop, and shed properly. Your skin is constantly renewing itself, and vitamin D helps keep this process running smoothly. Without enough of it, your skin may struggle to stay hydrated, leading to dryness, irritation, and a weaker protective barrier. This can make your skin more sensitive, inflamed, and prone to conditions like eczema, acne, or redness.
A deficiency in vitamin D can contribute to:
- increased inflammation
- weakened skin barrier
- slower skin healing
- higher susceptibility to skin conditions (5)
Common Skin Conditions Linked to Vitamin D Deficiency
Research suggests that low vitamin D levels may contribute to several common skin conditions (6), from dryness and irritation to more serious inflammatory issues.
- Skin Cancer: Vitamin D plays a role in protecting cells from abnormal growth. Some studies suggest that it may help lower the risk of certain cancers, including skin cancer (7, 8), by regulating cell growth and preventing harmful cells from spreading.
- Psoriasis: This condition causes the skin to produce new cells too quickly, leading to thick, scaly patches. Vitamin D helps slow this process down and reduces inflammation, which can improve psoriasis symptoms (9).
- Acne: Acne happens when the immune system overreacts to bacteria on the skin, causing inflammation and breakouts. Research has shown that vitamin D levels are negatively correlated with acne severity (10).
- Vitiligo: This condition occurs when skin loses its natural pigment, creating white patches. Vitamin D may help protect the pigment-producing cells and prevent the immune system from attacking them.
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): People with eczema often have low vitamin D levels (11), which can weaken the skin’s protective barrier. Vitamin D helps strengthen the skin and reduce inflammation, making symptoms like itching and redness more manageable.
Omega 3 and Vitamin D: Working Together For Healthy Skin
In the 17th century, cod liver oil was used as a natural remedy for various ailments, long before scientists understood its role in providing essential vitamin D. Today, vitamin D recommendations are still based on the amount found in just one tablespoon of raw cod liver oil. But cod liver oil isn’t just a source of vitamin D—it’s also rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which play a critical role in maintaining healthy skin.
Environmental pollutants like air pollution, detergents, cigarette smoke, and microplastics have been shown to weaken the skin’s natural barrier (12), leading to inflammation, dryness, and sensitivity. This damage makes skin more prone to eczema, acne, and premature aging, as the skin struggles to defend itself and heal properly.
Research suggests that omega-3 fatty acids (EPA and DHA) and vitamin D work together to strengthen the skin barrier and fight inflammation (13), helping to counteract the effects of environmental stressors.
Omega-3s, particularly EPA and DHA, have been found to:
- Strengthen the skin barrier
- Reduce inflammation
- Support skin healing
- Protect against UV damage
At the same time, vitamin D helps regulate skin cell turnover, supports the immune system, and promotes skin repair. When combined, these nutrients work to keep the skin hydrated, smooth, and more resilient against environmental damage.
Why a Strong Skin Barrier Matters

A healthy skin barrier is essential for protecting against dryness, irritation, and inflammation. But modern environmental factors, including pollution and increased UV exposure, can weaken this defense system. When the skin barrier is compromised, moisture escapes more easily, and irritants penetrate more deeply, leading to conditions like eczema, acne, and premature aging.
Omega-3 fatty acids, especially EPA and DHA, play a critical role in restoring and strengthening the skin’s barrier function (14). These essential fats help seal in hydration, protect against pollutants, and minimize irritation from UV exposure. EPA and DHA can reduce inflammation, reinforce the skin’s protective lipid layer, and support faster skin repair—all of which are key to maintaining resilient, healthy skin in the face of environmental stressors.
How to Ensure Adequate Vitamin D and Omega 3 Intake
Getting enough vitamin D and omega-3s is essential for maintaining healthy skin, but many people don’t get enough from diet alone.
While our bodies can produce vitamin D3 when exposed to sunlight, factors like age, BMI, skin tone, geographic location, and sunscreen use can reduce how much is absorbed (15). Similarly, omega-3s—particularly EPA and DHA, which provide the most skin benefits—are primarily found in fatty fish, making supplementation necessary for many people.
Vitamin D3 is not technically a vitamin—it’s a hormone that our bodies produce when exposed to UVB rays. However, several factors can limit vitamin D production, including:
- Darker skin tones: melanin reduces vitamin D synthesis
- Living in northern latitudes: above Atlanta, GA, between November and March
- Aging: older skin is less efficient at converting sunlight into vitamin D
- Time of day and season: early morning and winter months provide less UVB exposure
- Sunscreen use: while important for skin protection, it can block vitamin D synthesis
To maintain healthy levels, try to incorporate sun exposure in moderation and eat vitamin D-rich foods, such as:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
- Fortified foods (dairy, plant-based milk, cereals)
- Egg yolks
In cases of deficiency, taking vitamin D supplements can be an effective way to restore optimal levels.
Best Sources of Omega-3s
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential, meaning our bodies can’t make them—we must get them from food or from high-quality omega-3 supplements. The best sources include:
- Fatty fish (salmon, sardines, mackerel, anchovies)
- Seaweed (one of the rare plant-based sources of EPA and DHA)
- Flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts (which contain ALA, a plant-based omega-3)
Since the majority of people don’t consume enough omega-3-rich foods, supplementation is often the best option to ensure adequate intake.
Supplementing for Optimal Skin Health
With vitamin D and omega-3s, supplements can help fill the gap if your dietary intake is low. Here’s what experts recommend:
- Vitamin D3: Because there are so many variables that influence vitamin D levels, it can be wise to take a blood test to start and then correct from there. Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the right dosage for your needs.
- Omega-3s (EPA/DHA): For adults looking to support their lipid levels and reduce inflammation, 2000–3000 mg of EPA/DHA per day is typically required. For skin health specifically, there are also topical formulations, like Barristrong cream, which can be applied directly to the skin.
Does Vitamin D3 Brighten Skin?

Because vitamin D3 regulates skin cell turnover and reduces inflammation, it can help improve uneven skin tone, redness, and dullness. Inadequate vitamin D intake has been linked to dry, irritated skin and conditions like eczema and acne, which can make the skin appear lackluster and uneven. By supporting skin repair and strengthening the barrier, vitamin D3 helps keep your skin looking smooth, clear, and vibrant.
If your skin appears dull or irritated, ensuring you get enough vitamin D through sun exposure, diet, or dietary supplements or skincare products with vitamin D may help improve its overall tone and texture, giving you a naturally healthy glow.
- Sizar O, Khare S, Goyal A, Bansal P, Givler A. Vitamin D Deficiency. PubMed. Published July 17, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532266/
- Bocheva G, Slominski RM, Slominski AT. The Impact of Vitamin D on Skin Aging. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021;22(16):9097. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22169097
- Schauber J, Gallo RL. The vitamin D pathway: a new target for control of the skin’s immune response? Experimental Dermatology. 2008;17(8):633-639. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0625.2008.00768.x
- Berridge MJ. Vitamin D deficiency accelerates ageing and age-related diseases: a novel hypothesis. The Journal of Physiology. 2017;595(22):6825-6836. doi:https://doi.org/10.1113/jp274887
- Umar M, Sastry KS, Al Ali F, Al-Khulaifi M, Wang E, Chouchane AI. Vitamin D and the Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Skin Pharmacology and Physiology. 2018;31(2):74-86. doi:https://doi.org/10.1159/000485132
- Mostafa WZ, Hegazy RA. Vitamin D and the skin: Focus on a complex relationship: A review. Journal of Advanced Research. 2015;6(6):793-804. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2014.01.011
- Wyatt C, Neale RE, Lucas RM. Skin cancer and vitamin D: an update. Melanoma Management. 2015;2(1):51-61. doi:https://doi.org/10.2217/mmt.14.31
- Martin-Gorgojo A, Gilaberte Y, Nagore E. Vitamin D and Skin Cancer: An Epidemiological, Patient-Centered Update and Review. Nutrients. 2021;13(12):4292. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124292
- Mahtani R, Nair PMK. Daily oral vitamin D3 without concomitant therapy in the management of psoriasis: A case series. Clinical Immunology Communications. 2022;2:17-22. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clicom.2022.01.001
- Hasamoh Y, Thadanipon K, Juntongjin P. Association between Vitamin D Level and Acne, and Correlation with Disease Severity: A Meta-Analysis. Dermatology (Basel, Switzerland). Published online August 4, 2021:1-8. doi:https://doi.org/10.1159/000517514
- Palmer DJ. Vitamin D and the Development of Atopic Eczema. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2015;4(5):1036-1050. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm4051036
- Pat Y, Duygu Yazici, Paolo D’Avino, et al. Recent advances in the epithelial barrier theory. International Immunology. 2024;36(5):211-222. doi:https://doi.org/10.1093/intimm/dxae002
- Huang TH, Wang PW, Yang SC, Chou WL, Fang JY. Cosmetic and Therapeutic Applications of Fish Oil’s Fatty Acids on the Skin. Marine Drugs. 2018;16(8):256. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/md16080256
- Parke MA, Perez-Sanchez A, Zamil DH, Katta R. Diet and Skin Barrier: The Role of Dietary Interventions on Skin Barrier Function. Dermatology Practical & Conceptual. 2021;11(1):e2021132. doi:https://doi.org/10.5826/dpc.1101a132
- Maurya VK, Aggarwal M. Factors influencing the absorption of vitamin D in GIT: an overview. Journal of Food Science and Technology. 2017;54(12):3753-3765. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2840-0
Popular posts


Related posts