Omega-3 & Pain Relief: Finding the Best Strategy
Are you one among the 1 in 5 Americans grappling with chronic pain, as reported by the CDC [1]?
If the thought of traditional pain medications and their potential side effects worries you, you’re not alone. It’s a valid concern, given the risks of gastrointestinal problems and addiction linked to these drugs.
But, here’s some good news: Omega-3 fish oil is a natural anti-inflammatory aid that may ease chronic discomfort. The key lies in getting the right dose and quality.
Omega-3 Fish Oil and Pain Relief
Scientists have studied the link between omega-3 fatty acids and pain relief since the 1980s [2]. Over the years, numerous clinical trials have found that omega-3 supplements may lower pain scores and reduce the need for pain-relieving medications.
This makes sense from a biological standpoint. The two best-researched omega-3 fatty acids, EPA and DHA work on the same molecular targets as Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) [3].
Of course, EPA and DHA don’t work as fast as pain killers. These fatty acids have to build up sufficiently in the cell membrane, which can take weeks or even months [4]. As a long-term strategy, however, omega-3s have few downsides.
With that said, omega-3 benefits depend on getting enough. To understand the kinds of doses needed to achieve results, let’s look at the research on rheumatoid arthritis:
Omega-3 Fish Oil & Rheumatoid Arthritis Research
In omega-3 studies, rheumatoid arthritis patients have historically had to swallow a lot of fish oil capsules.
Take this placebo-controlled trial from 2008 as an example. In it, patients took 10 cod liver oil capsules daily, amounting to 2200 mg of EPA/DHA. Almost 40% of patients reduced their use of NSAIDs by more than 30%. But as the authors noted, many patients withdrew from the study early because they did not like swallowing so many capsules [5].
Similar doses, however, have been reiterated in later research. A 2012 meta-analysis found that giving RA patients at least 2700 mg of EPA/DHA daily for over 3 months reduced their need for NSAIDs [6].
A 2017 systematic review also concluded that daily doses ranging 3000 – 6000 mg of omega-3s had the greatest pain relief potential [7].
How Much EPA/DHA Do Typical Omega-3 Capsules Contain?
Regular fish oil capsules often provide less omega-3s than people expect. Many products advertise that they contain 1000 mg of fish or krill oil, giving the impression of a substantial dose. But in natural oils, only a small part of that total is EPA and DHA.
To see how much EPA and DHA you actually get per serving, check the nutrition facts.
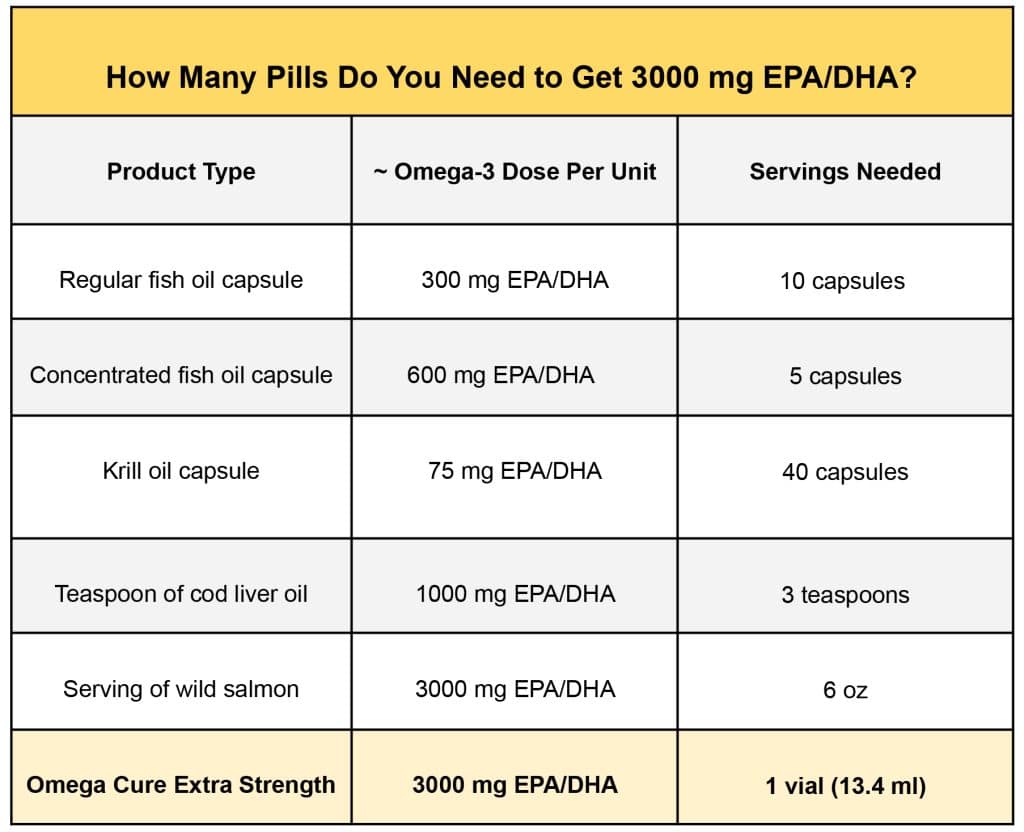
Hard to swallow: With regular omega-3 capsules, it can be hard to get enough EPA and DHA omega-3s for good results.
Can You Eat Your Way to Enough Omega-3s?
Eating fish like salmon, sardines, and herring is a great way to get more omega-3s. But for rheumatoid arthritis, two studies say eating an anti-inflammatory diet and taking omega-3 supplements might work better than just changing your diet [8].
Omega-3s and Osteoarthritis
While there is ample research on rheumatoid arthritis, there’s less high-quality data about how omega-3s impact osteoarthritis. The research available is also more mixed. For instance, a 2017 meta-analysis found that while omega-3 fish oils showed potential for reducing arthritis pain, the results did not reach statistical significance for osteoarthritis patients specifically [9].
More recent trials though are finding a stronger connection. Meta-analyses from 2023 and 2021 both found that omega-3s reduced pain in osteoarthritis patients [10, 11].
Benefits Besides Pain Relief
Besides potentially reducing pain and inflammation, omega-3s may offer more benefits for those with arthritis.
Cell and animal studies suggest omega-3s can slow joint degeneration and cartilage loss [12]. While these results need to be replicated in clinical trials, it’s an exciting prospect.
Full-spectrum omega-3s also help cells work better and provide healthy fatty acids for our gut bacteria. For those reasons, they might make certain medications more effective and decrease side effects, like ulcers [13, 14]. Indeed, some scientists are exploring the potential use of omega-3s for combating the harms of opioid use [15, 16] – although clinical trials are still needed.
An Effective Omega-3 Dose Is Crucial
While fish oil’s pain relieving effects have been recognized for some time, few people – including physicians – understand the doses required for results [17].
Sadly, patients often miss an opportunity to improve their quality of life because they are taking ineffective amounts.
The Easiest Way to Get Your Daily EPA/DHA
At Omega3 Innovations, it’s our goal to help people get the omega-3s needed to actually feel better. That’s why we created Omega Cure® Extra Strength. Each vial provides 3000 mg of EPA/DHA in a convenient liquid form that you can drink.
Taking Omega Cure Extra Strength is simpler and more effective than swallowing 10 fish oil capsules. Additionally, the oil boasts exceptional freshness levels, a crucial factor for achieving optimal outcomes.
Based on our research, we’ve found that customers experience the best effects when taking 1 – 2 vials of Omega Cure Extra Strength daily for at least 12 weeks. This protocol matches the dose and time period noted in the studies above.
While omega-3s aren’t a silver bullet, we firmly believe getting enough of these essential fatty acids can improve quality of life for many. As the producers of the freshest, full-spectrum omega-3 oil on the market, we look forward to helping you live your best life, with more comfort and ease.
An Effective Omega-3 Dose, Made Simple
Experience the Omega3 Innovations difference for yourself with the most effective fish oil supplement on the market.
Buy Now
References:
1. Kuehn, B. (2018). Chronic Pain Prevalence. JAMA, 320 (16), 1632.
2. Navarini, L., Afeltra, A., Gallo Afflitto, G., & Margiotta, D. (2017). Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: Any Role in Rheumatoid Arthritis? Lipids in Health and Disease, 16(1), 197.
3. Proudman, S. M,, James, M. J., Spargo, L. D., et al (2015). Fish Oil in Recent Onset Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Randomised, Double-Blind Controlled Trial within Algorithm-Based Drug Use. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 74, 89-95.
4. Ye, J., & Ghosh, S. (2018). Omega-3 PUFA vs. NSAIDs for Preventing Cardiac Inflammation. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine, 5, 146.
5. Galarraga, B., Ho, M., Youssef, H. M., et al. (2008). Cod Liver Oil (N-3 Fatty Acids) as an Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug Sparing Agent in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology, 47(5), 665–669.
6. Lee, Y. H., Bae, S. C., Song, G. G. (2012). Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis. Archives of Medical Research, 43(5), 356-362.
7. Abdulrazaq, M., Innes, J. K., Calder, P. C. (2017). Effect of ω-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Arthritic Pain: A Systematic Review. Nutrition, 39-40: 57-66.
8. Raad, T., Griffin, A., George, E. S., Larkin, L., Fraser, A., Kennedy, N., & Tierney, A. C. (2021). Dietary Interventions with or without Omega-3 Supplementation for the Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review. Nutrients, 13(10), 3506.
9. Senftleber, N. K., Nielsen, S. M., Andersen, J. R., et al. (2017). Marine Oil Supplements for Arthritis Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. Nutrients, 9(1), 42.
10. Deng, W., Yi, Z., Yin, E., Lu, R., You, H., & Yuan, X. (2023). Effect of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Supplementation for Patients with Osteoarthritis: A Meta-Analysis. Journal of Orthopedic Surgery and Research, 18(1), 381.
11. Bahamondes, M. A., Valdés, C., & Moncada, G. (2021). Effect of Omega-3 on Painful Symptoms of Patients with Osteoarthritis of the Synovial joints: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology, 132(3), 297–306.
12. Oppedisano, F., Bulotta, R. M., Maiuolo, J., Gliozzi, M., Musolino, V., Carresi, C., Ilari, S., Serra, M., Muscoli, C., Gratteri, S., Palma, E., & Mollace, V. (2021). The Role of Nutraceuticals in Osteoarthritis Prevention and Treatment: Focus on N-3 PUFAs. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2021, 4878562.
13. Laino, C. H., Fonseca, C., Sterin-Speziale, N., Slobodianik, N., Reinés, A. (2010). Potentiation of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Antidepressant-Like Effects with Low Non-Antidepressant Doses of Fluoxetine and Mirtazapine. European Journal of Pharmacology, 648 (1 – 3),117 – 126.
14. Park, J. M., Han, Y. M., Jeong, M. et al. (2015). Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids as an Angelus Custos to Rescue Patients from NSAID-Induced Gastroduodenal Damage. Journal of Gastroenterology, 50, 614–625.
15. Hakimian, J., Minasyan, A., Zhe-Ying, L., et al. (2017). Specific Behavioral and Cellular Adaptations Induced by Chronic Morphine Are Reduced by Dietary Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. PloS One, 12(4), e0175090.
16. Hakimian, J. K., Dong, T. S., Barahona, J. A., et al. (2019). Dietary Supplementation with Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Reduces Opioid-Seeking Behaviors and Alters the Gut Microbiome. Nutrients, 11(8), 1900.
17. Hill, C. et al. (2009). The Use of Fish Oil in the Community: Results of a Population-Based Study. Rheumatology, 48(4), 441-2.
Popular posts


Related posts