The Effects of Fresh Omega-3 on Pregnancy and Postpartum Depression
Back when my daughter was in middle school, my husband Bo and I gave a lecture to her science class about how omega-3s work in the body. To my then 12-year-old daughter’s embarrassment, we didn’t shy away from mentioning how these fatty acids influence fertility and pregnancy.
Over a decade later, a flood of new studies have given us a clearer picture of how omega-3s impact everything from brain development to postpartum depression.
While scientists are uncovering big benefits, they’re also demonstrating that it’s important to pay attention to the quality and fatty acid composition of the oil.
How Brain Health Is Impacted by Omega-3s
Many people think of fish and fish oil as “brain food.” And in fact, many scientists have researched how prenatal omega-3s influence a baby’s brain development. To date, a number of studies have shown that omega-3 supplementation during pregnancy later improved children’s hand-eye coordination, focus, and problem solving skills (1), although these results have not always been consistently replicated.
In addition, getting too little omega-3 could be detrimental for the fetus’ developing brain. One 2018 animal study from France, for example, found that omega-3 deficiency during pregnancy negatively impacted the memory performance of adult offspring (2).
While omega-3 fatty acids are found in every cell of the human body, they are especially plentiful in the brain and eyes. For instance, fatty acids account for about 60% of the dry weight of the brain, with much of that coming from the omega-3 molecule DHA (1).
DHA is the omega-3 fatty acid best associated with brain development. But other types of omega-3s are also important to consume during pregnancy.
How Omega-3s Fight Inflammation
Aside from brain health, recent research has become increasingly focused on how omega-3s impact maternal inflammation during pregnancy. This is important since higher rates of inflammation are also associated with worse pregnancy outcomes, especially among overweight women (3, 4). In particular, inflammation during pregnancy has been linked with a greater likelihood of developing preeclampsia (5), postpartum depression (6), having a premature baby (7), and having a child with mental illness (8).
There are a couple of theories for why omega-3s help to reduce inflammation during pregnancy. For one, studies show that omega-3s support the microbiome and help inhibit certain types of inflammation-producing bacteria (9).
More research has shown that the omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA act as substrates for important molecules called “protectins” and “resolvins.” These molecules do exactly what they their names imply: They help resolve and protect against inflammation (10).
Can Omega-3s Reduce the Risk of Premature Birth?
Although the causes of preterm birth are complex and varied, scientists believe that in many cases, inflammation may be a contributing factor.
Research consistently demonstrates that women with lower blood levels of omega-3s have a higher risk of delivering prematurely than women with higher blood levels of these fatty acids. For instance, a big 2018 review of the omega-3 research to date found that women with increased intakes of omega-3s had an 11% lower risk of having their baby born less than 37 weeks out, and a 42% lower risk of having their baby born less than 34 weeks after conception (11).
Potentially reducing the risk of giving birth prematurely is great news: Preterm birth impacts approximately 1 in 10 babies born in the United States and is the leading cause of death for children under age 5 worldwide (11).
Importance of Maintaining Omega-3 Intake During the Third Trimester
In spite of the pivotal roles that omega-3s play during pregnancy, most pregnant women simply don’t get enough of these beneficial fatty acids. Surveys find that up to 95% of child-bearing-age women and pregnant women don’t meet the recommendations for EPA and DHA omega-3 intake (1).
To make matters worse, researchers have also found that most mothers’ omega-3 index levels typically decrease over the course of their pregnancy, especially during the last trimester. Since the third trimester is when the growing fetus needs more omega-3s for its rapidly-growing brain and retinae (12), it’s important for the mother to be vigilant about her intake.
The vast majority of pregnant women in the United States do not eat enough omega-3-rich fatty fish (like sardines) during pregnancy. That’s why finding a fresh omega-3 supplement is critical.
How Much Omega-3 Do Pregnant Women Need?
There are many different opinions and recommendations about how much omega-3 a pregnant person should consume. For instance, the American Pregnancy Association recommends getting 300 mg DHA daily as a minimum. Other groups place the recommendation higher at 520 mg of EPA/DHA per day (13). And in studies, researchers often use even higher doses, even going up to 3300 mg of EPA/DHA daily (1).
The Link Between Omega-3 Deficiency & Postpartum Depression
Higher intakes of omega-3 fatty acids isn’t just important during pregnancy, but also while breastfeeding and for managing conditions like postpartum depression.
Healthcare professionals believe that between 10 to 15% of mothers experience postpartum depression symptoms (14), like severe mood swings, excessive fatigue, and bonding difficulties. Although the reasons why women develop postpartum depression are complex, we do know that diet plays a role.
A 2019 study from Belgium found that women with an omega-3 index below 5% were 5 times more likely to have a depressive episode than mothers with omega-3 indexes above 5% (15).
All Omega-3 Oils Are Not Made Equally
Since most people don’t get enough omega-3s from their diet, finding a healthful supplement is a must. However, when considering a prenatal omega-3 supplement, it’s important to be aware of the oil’s quality.
Today, most omega-3 supplements are carefully purified to remove mercury and pollutants (that’s one big benefit that fish oil has over eating fish). Unfortunately, studies from Canada (16), Norway (17), New Zealand (18) and South Africa (19) have consistently found that the majority of omega-3 supplements sold at retail stores exceed international freshness standards – long before their stated expiration dates.
Concerningly, numerous studies show that consuming rancid omega-3 oils could be more harmful than helpful. In fact, one 2016 study found that when rats were given rancid fish oil, it increased maternal insulin resistance, as well as the mortality rates of the babies (20)!
Is My Omega-3 Supplement Fresh?
Since expiration dates are unreliable, what is the best way to determine whether your prenatal omega-3 supplement is fresh or rancid?
On principle, be wary of using any gelatin fish oil capsules without first breaking them open and tasting/smelling the oil inside. Also be sure to stay clear of products that use heavy flavoring, which is how the industry conceals bad-tasting, rancid oil.
The best way for consumers to assess freshness is to taste and/or smell it. If your oil smells or tastes pungent, it has oxidized and should be thrown away. Omega3 Innovations’ liquid fish oil tastes just like fresh fish (in other words, not fishy at all).
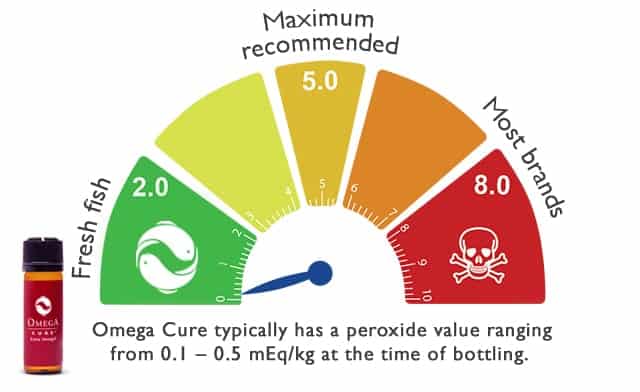
To assess whether an omega-3 supplement is good, you can also check the brand’s freshness measurements (peroxide and anisidine values).
Getting a Full-Spectrum Prenatal Supplement
In the world of prenatal nutrition, the omega-3 fatty acid DHA typically gets all the glory. At face value, this makes sense: DHA is the most prevalent omega-3 fatty acid in the brain.
DHA, however, is just one member of the omega-3 family. In fish and full-spectrum fish oils, DHA is naturally found with a whole range of other omega-3s, including EPA, ALA, and DPA. All of these fatty acids play unique roles in the cells and also work synergistically.
So while DHA might be crucial for brain development, research indicates that EPA may be a more powerful mediator of cellular inflammation, including in the brain (21). This could help explain why a 2018 review found that, while EPA supplementation effectively reduced some symptoms of postpartum depression, DHA supplementation did not have the same benefits for lactating women (22).
It’s also worth remembering that creating DHA-only supplements typically requires more processing and chemical manipulation than natural oils containing the full range of the omega-3 family. The more chemically manipulated an oil is, the less stable it becomes, potentially leading to rancidity problems.
Choose Omega3 Innovations for Your Family
At Omega3 Innovations, your health is of the utmost importance. That is why we produce a carefully purified, full-spectrum omega-3 oil with the best freshness measurements on the market. Omega Cure® has no fishy taste or smell, making it easy to drink straight or add into juices, yogurts and smoothies. And for those who struggle to swallow oily textures, we also make omega-3 and fiber-rich cookies that contain high doses of both EPA and DHA.
Whichever of these options you choose, you deserve to have a high quality omega-3 product. We look forward to contributing to the health of you and your future family.
Try Exceptionally Fresh Omega Cure
Experience the Omega3 Innovations difference for yourself with the most effective fish oil supplement on the market.
Buy Now
References:
1. Devarshi, P. P., Grant, R. W., Ikonte, C. J., & Hazels Mitmesser, S. (2019). Maternal Omega-3 Nutrition, Placental Transfer and Fetal Brain Development in Gestational Diabetes and Preeclampsia. Nutrients, 11(5), 1107.
2. Labrousse, V.F., Leyrolle, Q., Amadieu, C. et al. (2018). Dietary Omega-3 Deficiency Exacerbates Inflammation and Reveals Spatial Memory Deficits in Mice Exposed to Lipopolysaccharide During Gestation. Brain, Behavior & Immunity, 73: 427-440.
3. Penfield-Cyrm, A., Monthe-Drez, C., Smid, & M.C., Sen, S. (2018). Maternal BMI, Mid-Pregnancy Fatty Acid Concentrations,and Perinatal Outcomes. Clinical Therapeutics, 40(10): 1659-1667.
4. McCullough, L. E., Miller, E. E., Calderwood, L. E., et al. (2017). Maternal Inflammatory Diet and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes. Epigenetics, 12(8), 688–697.
5. Cornelius, D. C. (2018). Preeclampsia: From Inflammation to Immunoregulation. Clinical medicine insights. Blood Disorders, 11, 1179545X17752325.
6. Kendall-Tackett, K. (2007). A New Paradigm for Depression in New Mothers: The Central Role of Inflammation and How Breastfeeding and Anti-Inflammatory Treatments Protect Maternal Mental Health. International Breastfeeding Journal, 2, 6.
7. Cappelletti, M., Della Bella, S., Ferrazzi, E., Mavilio, D., & Divanovic, S. (2016). Inflammation and Preterm Birth. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 99(1):67-78.
8. Brawley, T. (2018). Study Confirms That Inflammation During Pregnancy Is Linked to Baby’s Brain. Oregon Health & Science University.
9. Garcia-So, J., Zhang, X., Yang, X., et al. (2019). Omega-3 Fatty Acids Suppress Fusobacterium Nucleatum-Induced Placental Inflammation Originating from Maternal Endothelial Cells. JCI Insight, 4(3), e125436.
10. Jones, M. L., Mark, P. J., Keelan, J. A., et al. (2013). Maternal Dietary Omega-3 Fatty Acid Intake Increases Resolvin and Protectin Levels in the Rat Placenta. Journal of Lipid Research, 54(8), 2247–2254.
11. (2018). New Research Finds Omega-3 Fatty Acids Reduce the Risk of Premature Birth. Cochrane.
12. Burchakov, D. I., Kuznetsova, I. V., & Uspenskaya, Y. B. (2017). Omega-3 Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Preeclampsia: Trials Say “No,” but Is It the Final Word?. Nutrients, 9(12), 1364.
13. Thompson, M., Hein, N., Hanson, C., et al. (2019). Omega-3 Fatty Acid Intake by Age, Gender, and Pregnancy Status in the United States: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2003-2014. Nutrients, 11(1), 177.
14. Arbabi, L., Baharuldin, M.T., Moklas, M.A., Fakurazi, S., & Muhammad, S.I. (2014). Antidepressant-Like Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Postpartum Model of Depression in Rats. Behavioural Brain Research, 271:65-71.
15. Hoge, A., Tabar, V., Donneau, A. F., et al. (2019). Imbalance Between Omega-6 and Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Early Pregnancy Is Predictive of Postpartum Depression in a Belgian Cohort. Nutrients, 11(4), 876.
16. Jackowski, S. A., Alvi, A. Z., Mirajkar, A., Imani, Z., Gamalevych, Y., Shaikh, N. A., & Jackowski, G. (2015). Oxidation Levels of North American Over-the-Counter N-3 (Omega-3) Supplements and the Influence of Supplement Formulation and Delivery Form on Evaluating Oxidative Safety. Journal of Nutritional Science, 4, e30.
17. Laupsa-Borge, J. (2012). Velg Ferske og Naturlige Omega-3 Produkter. Helsemagasinet Vitenskap & Fornuft.
18. Albert, B. B. et al. (2015). Fish oil Supplements in New Zealand Are Highly Oxidised and Do Not Meet Label Content of N-3 PUFA. Scientific Reports 5, 7928.
19. Opperman, M., & Benade, S. (2013). Analysis of the Omega-3 Fatty Acid Content of South African Fish Oil Supplements: A Follow-Up Study. Cardiovascular Journal of Africa, 24(8), 297–302.
20. Albert, B.B. et al. (2016). Oxidized Fish Oil in Rat Pregnancy Causes High Newborn Mortality and Increases Maternal Insulin Resistance. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative, and Comparative Physiology, 311(3): R497-504.
21. Sears, B. (2012). What Are the Real Differences Between EPA and DHA? Psychology Today.
22. Hsu, M.C., Tung, C.Y., & Chen, H.E. (2018). Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation in Prevention and Treatment of Maternal Depression: Putative Mechanism and Recommendation. Journal of Affective Disorders, 238:47-61.
Popular posts


Related posts