What Does Fish Oil Do for Men?
If you’re a man looking to optimize your health, adding a fish oil supplement to your daily regimen could be a game changer. Packed with omega-3 fatty acids, fish oil offers many benefits for men’s health needs.
What does fish oil do for men, specifically? From supporting sperm health to potentially boosting muscle recovery, reducing inflammation, and lowering blood pressure, this powerful supplement is worth considering. But what exactly makes taking fish oil supplements so beneficial, and how much fish oil do most men need?
We’ll share details on how fish oil impacts key men’s health issues, including sperm health, joint and muscle health, and cardiovascular risk factors like triglyceride levels and blood pressure. We’ll also give you an overview of how much fish oil most men need to see optimal benefits.
Why Should Men Take Fish Oil?
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential healthy fats that must be obtained through foods such as fatty fish or by taking fish oil supplements. They are vital for the optimal functioning of every cell in your body.
Studies show that an estimated 95% of Americans—men, in particular—have seriously deficient omega-3 levels, putting them at a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, stroke and dying early [1, 2].
Of the foods we eat, only certain types of oily fish and full-spectrum fish oils contain the full range of the omega-3 fatty acid family. Two of these include eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). These fatty acids are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and their ability to support heart, brain, and joint health.
EPA and DHA can be obtained by eating fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and anchovies. But if you don’t eat those types of fish at least twice weekly, fish oil supplement use can be a good way to boost your intake.
Fish Oil Supplement Use and Sperm Health
Male infertility is a growing concern. Sperm count in Western men has dropped by 50% since 1970, and this decline continues to rise.
Fortunately, omega-3 fatty acids have shown promise in improving sperm health. A 2019 study showed a positive relationship between dietary fish oil supplementation and semen quality in infertile men [3]. Another study found that a 3-month intervention of omega-3s, combined with other vitamins, significantly reduced harmful sperm DNA fragmentation levels, which is a key indicator of male infertility [4].
How does consuming fish oil help improve sperm health? Sperm contains a significant amount of omega-3 fatty acids, just like the brain and the eyes. In particular, DHA is necessary for binding the building blocks of the acrosome at the tip of the sperm cell together, which allows the sperm to break down the walls of the ovum.
The DHA found in fish oils also affects the physical properties of sperm, providing the fluidity needed for proper movement.
How Do Omega 3 Fatty Acids Affect Performance and Recovery?
Studies suggest that EPA and DHA fatty acids can boost endurance and help muscles recover faster after exercise [5, 6]. Studies show that both athletes and amateurs see more significant benefits the longer they use fish oil supplements.
Fish oil benefits from these studies include:
• Improved Performance: Better neuromuscular function leads to enhanced athletic performance.
• Enhanced Recovery: Omega-3s support the immune system and reduces oxidative stress, protecting cells from damage by free radicals.
• Illness/Injury Protection: Fish oil may protect against exercise-induced bronchitis and traumatic brain injury (TBI), which is especially relevant for men involved in sports like American football.
With regard to TBI, DHA and EPA show promise in repairing neurons based on lab tests and animal studies. The exact mechanisms are not fully understood, but DHA in brain cells seem to aid in healing brain injuries and reducing long-term effects. DHA may also protect the brain by maintaining myelin, lowering harmful glutamate levels, preventing mitochondrial damage, and regulating specific receptors.
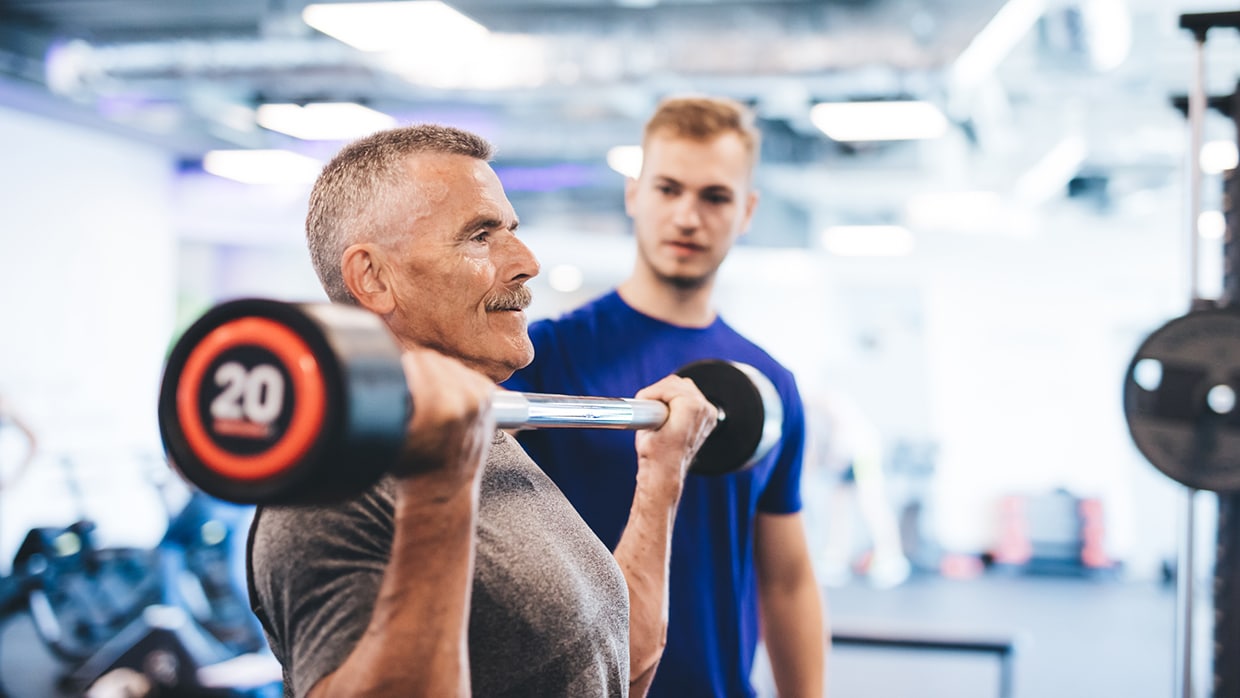

Muscle boost: Some studies show that taking omega-3s may improve muscle retention in older age.
Muscle Recovery
If you’re struggling with muscle recovery after your workouts, fish oil supplements could be smart to add to your daily routine.
The frequency, intensity, and length of your workouts all play a part in how you recover. After a light workout, 24 hours of rest is usually sufficient. But when you’re still struggling with delayed muscle soreness two or three days after an intense workout session, it can be difficult to keep the muscle-building momentum going.
This is where omega-3s come in. A number of studies have shown that taking fish oil can reduce muscle soreness thanks to their anti-inflammatory benefits. Omega-3s may also reduce the risk of muscle cell injury during heavy exercise by improving the elasticity and flexibility of the cells [7, 8].
Using a high quality fish oil like Omega Cure® can speed up recovery time after a workout. It gives a clear advantage for men who are after that Arnold Schwarzenegger kind of physique.
Muscle Loss in Aging Men
As men age, muscle loss often becomes a problem. Even if you work out, your body produces less testosterone to help build new muscle, making it harder to see gains. The good news is there are some promising studies that show omega-3s can help with muscle retention.
A 2020 meta-analysis of 10 trials showed that taking over 2000 mg of omega-3s daily led to a 0.73-pound muscle mass increase in elderly individuals and improved walking speed after six months of supplementation. These gains may seem minor, but they’re actually quite hopeful when you consider that people over 50 lose about 2% of their muscle mass each year.
Previous studies support these findings. For instance, a 2015 study found that giving healthy older individuals 3360 mg of EPA/DHA omega-3s daily for six months increased thigh muscle volume, handgrip strength, and one-repetition muscle strength, effectively preventing 2-3 years’ worth of typical age-related muscle loss.
Brain Health
Research shows that animals given omega-3 fatty acids are better equipped to handle traumatic brain injuries (TBIs). They recover both functionally and biologically, even after experiencing multiple mild TBIs. These studies suggest that taking fish oil supplements regularly could help reduce brain damage from TBIs.
With this in mind, the US military is exploring ways to increase omega-3 levels in soldiers on active duty. I attended a conference where a general presented brain scans of a soldier with a TBI, taken before and after receiving a substantial dose of omega-3s and the improvements were impressive.
Omega 3 fatty acids also help maintain important molecules needed for learning, such as BDNF (Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor), synapsin I, and CREB (cAMP response element-binding protein). These molecules play crucial roles in brain health and cognitive function.
Joint Health
For many men, joint pain and stiffness can become a significant issue as they age. Omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil have been shown to help reduce inflammation, thereby alleviating symptoms associated with arthritis and other joint conditions. According to a study published in the Journal of Rheumatology, participants who took fish oil supplements experienced a significant reduction in joint pain and morning stiffness compared to those who did not.
Reduction in the Risk of Stroke
Cardiovascular health is a critical concern for men, especially as they age. Fish oil has been found to lower the risk of stroke by reducing blood clot formation and improving blood flow. A study conducted by the American Heart Association revealed that men who consumed omega-3-rich fish oil had a lower incidence of stroke and other cardiovascular events.
Lowering of Triglyceride Levels
Triglycerides are a type of fat linked to heart disease. While necessary for energy and bodily functions, excessive triglycerides (hypertriglyceridemia) can harm heart and blood vessels, raising the risk of cardiovascular disease. Levels above 200 mg/dL significantly increase the likelihood of dying from cardiovascular issues.
High triglycerides contribute to atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque builds up in the arteries, potentially leading to carotid artery disease, coronary artery disease, and peripheral artery disease, all of which can cause heart attacks or strokes over time.
High triglyceride levels are a major risk factor for heart disease. Omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil can effectively lower triglyceride levels, promoting better heart health. Research published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology indicates that taking between 3000–4000 mg of EPA/DHA can lead to a 25% reduction in triglyceride levels.
Colon Cancer
Research from the University of Massachusetts and the University of California, Davis, has found that omega-3 fatty acids, specifically DHA, can help fight colon cancer. When DHA is processed in the body, it creates compounds called EDPs, which play a key role in this process.
EDPs are effective at stopping the growth and spread of colon cancer by preventing the formation of new blood vessels that tumors need to grow. In both lab tests and studies with mice, EDPs blocked the development of these blood vessels and also stopped cancer cells from moving and forming the structures they need to spread.
Studies also show that increasing the intake of omega-3 fatty acids is linked to better survival rates in patients with stage III colorectal cancer. This suggests that a diet rich in omega-3s can have significant health benefits for cancer patients.
Additionally, omega-3s can enhance the effectiveness of cancer treatments and reduce their toxicity, making them a valuable addition to traditional cancer therapies.
Prostate Health
The prostate gland, a key part of the male reproductive system, often becomes enlarged or inflamed as men age. Studies suggest that omega-3 fatty acids (also known as n-3 PUFAs) might help protect against prostate cancer, while omega-6 fatty acids (n-6 PUFAs) could increase the risk. Most information about dietary fat and cancer comes from observational studies, which means they watch trends over time rather than conducting controlled experiments.
A controversial 2013 study from Ohio State University claimed that high levels of omega-3 fatty acids might increase the risk of prostate cancer. This caused a lot of concern about fish oil supplements. However, the study was widely criticized for its poor methods and odd findings. More recent research, including a review from Australia, found that omega-3s might actually reduce cancer risk and help with cancer treatment. Data from around the world show that populations with high omega-3 consumption, such as Japanese men, have lower rates of prostate cancer.
Mental Health
Omega-3s are highly concentrated in the brain and are essential for proper cognitive function. They have been linked to improved mood, reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety, and can even help manage symptoms of ADHD.
What I hear from mothers who give their sons Omega Cure is that it helps their children with impulse control. In a pilot study using Omega Cookies, we saw that children given an Omega Cookie per day had an easier time focusing on their work.
Aggressivity and Social Skills
There’s growing interest in “nutritional psychiatry” and how nutrition can improve mental health. Researchers have found that people with impulsive and aggressive behaviors often have low levels of EPA and DHA. This has led to studies on how these fatty acids, particularly during infancy and pregnancy, can impact behavior later in life.
Research shows that a lack of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and a high ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids are linked to aggressive and impulsive behaviors. Increasing omega-3 intake may help reduce hostility, aggression, and impulsivity by improving the function of the serotonin system and stabilizing cell membranes.
Blood Pressure
Most studies show that omega 3s have a slight blood pressure-lowering effect.
What’s most interesting is that these fatty acids significantly improve Pulse Wave Velocity. Pulse Wave Velocity is another way of measuring arteriosclerosis. Think of the arteries as tubes. When you eat the wrong kinds of fats, the walls become stiff. Pulse Wave measures the stiffness of the arterial wall.
Several meta-analyses using measurements from PWV indicate omega-3s make the arteria will become more flexible. This means that when you exercise, your cardiovascular system will have an easier time to adapt. At the same time, you lower your risk of heart attack and stroke.
How Much Fish Oil Do Most Men Need?

Keep in mind, there is no magic bullet that protects you from the stresses and demise of our Western lifestyle. Exercise, diet, getting enough sleep, and keeping in touch with friends and family are all important to good health. But again and again, research and anecdotal reports show that omega-3s potentiate these healthy lifestyle practices.
In the beginning, there was fish oil. We were the first to bring it to American shores – pure, natural, full-spectrum fish oil from Norway the way Mother Nature intended it ( not fragmented or chemically altered like most commercial oils)
Pharmaceutical companies have tried to duplicate nature’s EPA/DHA properties with synthetic, prescription omega-3, but as wise men know, following Mother Nature’s full-spectrum Omega Cure or Omega Cure Extra Strength is always the better choice.
Try Exceptionally Fresh Omega Cure
Experience the Omega3 Innovations difference for yourself with the most effective fish oil supplement on the market.
Buy Now
References:
1. Papanikolaou, Y., Brooks, J., Reider, C., & Fulgoni, V. L., 3rd (2014). U.S. Adults Are Not Meeting Recommended Levels for Fish and Omega-3 Fatty Acid Intake: Results of an Analysis Using Observational Data from NHANES 2003-2008. Nutrition Journal, 13, 31. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-13-31
2. Daniells, S. (2015, December 10). Could Widespread Low Omega-3 Levels Be Putting American Hearts at Risk? Nutra-Ingredients-USA. https://www.nutraingredients-usa.com/Article/2015/12/10/Vast-majority-of-Americans-have-low-Omega-3-Index
3. Skoracka, K., Eder, P., Łykowska-Szuber, L., Dobrowolska, A., & Krela-Kaźmierczak, I. (2020). Diet and Nutritional Factors in Male (In)fertility-Underestimated Factors. Journal of clinical medicine, 9(5), 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051400
4. Humaidan, P., Haahr, T. et al. (2022). The Combined Effect of Lifestyle Intervention and Antioxidant Therapy on Sperm DNA Fragmentation and Seminal Oxidative Stress in IVF patients: A Pilot Study. International Brazilian Journal of Urology, 48(1), 131–156. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2021.0604
5. Thielecke, F., & Blannin, A. (2020). Omega-3 Fatty Acids for Sport Performance-Are They Equally Beneficial for Athletes and Amateurs? A Narrative Review. Nutrients, 12(12), 3712. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123712
6. Kyriakidou, Y., Wood, C., Ferrier, C., Dolci, A., & Elliott, B. (2021). The Effect of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation on Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 18(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-020-00405-1
7. Gammone, M. A., Riccioni, G., Parrinello, G., & D’Orazio, N. (2018). Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: Benefits and Endpoints in Sport. Nutrients, 11(1), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010046
8. Lembke, P., Capodice, J., Hebert, K., & Swenson, T. (2014). Influence of Omega-3 (n3) Index on Performance and Wellbeing in Young Adults after Heavy Eccentric Exercise. Journal of Sports Science & Medicine, 13(1), 151–156.
Popular posts


Related posts