Does Olive Oil Have Enough Omega 3?
Olive oil has long been celebrated as a cornerstone of healthy diets, especially in Mediterranean cuisine. Its rich flavor and versatility make it a favorite in kitchens worldwide. Beyond its culinary appeal, olive oil is often praised for its health benefits, including its potential for preventing cardiovascular disease and reducing inflammation
But when it comes to omega-3 essential fatty acids—a type of fat critical for brain health, heart health, and reducing inflammation—does olive oil measure up? While it’s true that olive oil contains a small amount of omega-3s, it’s not nearly enough to meet your body’s needs.
Composition of Olive Oil
Olive oil is prized for its high content of monounsaturated fats (MUFA), particularly oleic acid, which makes up 55% to 83% of its fatty acids (1). Oleic acid has been linked to several health benefits, including reducing inflammation and supporting cardiovascular health.
In addition to its MUFA content, olive oil also contains minor yet powerful compounds like polyphenols, tocopherols, and phytosterols, which contribute to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Does olive oil have omega-3? When it comes to omega-3s, olive oil falls short. Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), the primary omega-3 fatty acid found in plant-based oils, makes up less than 1% of olive oil’s composition (1). While this amount is better than nothing, it’s far from sufficient to meet the body’s omega-3 needs. For comparison, other sources like flaxseed oil or fatty fish provide significantly higher amounts of omega-3s, making them better options for achieving an optimal balance of healthy fats.
Is Olive Oil Consumption Healthy?
Absolutely! Olive oil is a cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet, which has been linked to lower risks of heart disease, stroke, and even some cancers. Packed with monounsaturated fatty acids—around 75% by volume—olive oil can help reduce “bad” LDL cholesterol when used in place of saturated fats (2). Its antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds also contribute to its reputation as a heart-healthy, brain-friendly addition to your meals.
Comparing Olive Oil to Omega-3-Rich Sources
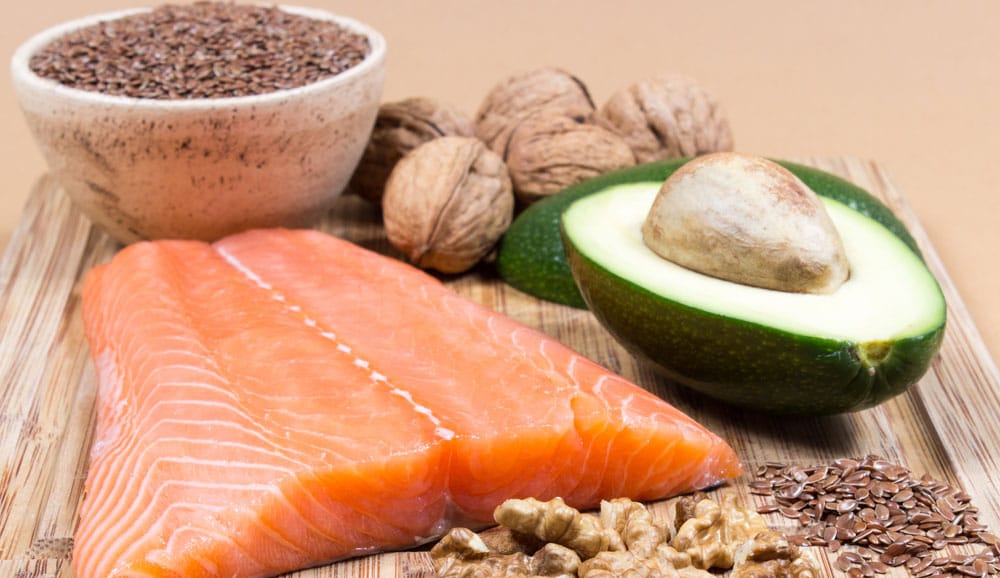

While olive oil has many other health benefits, it isn’t a significant source of omega-3s. Look for foods like fatty fish or a high-quality fish oil supplement to get your recommended daily dose of omega-3 fatty acids.
Olive oil has many health benefits, but it’s not a significant source of omega-3 fatty acids. A tablespoon of olive oil contains less than 1% alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), the plant-based form of omega-3s. Foods like salmon or sardines are far richer in omega-3s.
For example, a 3-ounce serving of salmon provides over 1,500 mg of EPA and DHA—omega-3s that offer powerful anti-inflammatory benefits. Chia seeds, while lacking EPA and DHA, deliver about 5,000 mg of ALA per ounce. Even walnuts offer more omega-3s than olive oil, with around 2,500 mg of ALA per ounce.
If your goal is to increase omega-3 intake, olive oil can complement omega-3-rich foods but shouldn’t be your primary source. Pairing olive oil with oily fish like salmon or a chia seed salad can help you enjoy the best of both worlds: heart-healthy monounsaturated fats from olive oil and the potent omega-3 benefits from other sources.
Health Benefits of Olive Oil Beyond Omega-3s

Olive oil offers a wide range of health benefits that extend far beyond its small omega-3 content. Rich in antioxidants and polyphenols, it has powerful anti-inflammatory and protective properties that support overall health.
Antioxidants and Polyphenols
The antioxidants and polyphenols found in olive oil are key players in reducing chronic inflammation and protecting cells from oxidative stress (3). These compounds have been linked to lower risks of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular issues, certain cancers, and neurodegenerative conditions. Research suggests they may also help regulate the immune system and support the body’s natural defenses against inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease (3).
Heart Health
Extra virgin olive oil is particularly celebrated for its role in improving heart health. Randomized trials have shown that extra virgin olive oil can reduce blood pressure, a major risk factor for coronary artery disease (4). It also supports healthy endothelial function (the lining of blood vessels) and improves cholesterol profiles by lowering LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels. These benefits help reduce the burden of heart disease while minimizing dependence on medications.
Skin and Cellular Health
Beyond internal health, olive oil’s antioxidant properties can benefit skin health by reducing inflammation and protecting against environmental stressors. Its ability to support cellular integrity contributes to overall vitality and longevity.
While olive oil isn’t a significant source of omega-3s, its combination of healthy monounsaturated fats, polyphenols, and antioxidants makes it a cornerstone of a balanced diet. For optimal health, pair it with foods rich in omega-3s to enjoy the best of both worlds.
How to Incorporate Omega-3 Essential Fatty Acids into a Diet with Olive Oil
Olive oil pairs beautifully with omega-3-rich foods, making it easy to boost your intake of healthy fats while enjoying delicious meals. By combining these powerhouse ingredients, you can follow a Mediterranean-inspired diet that supports heart health, reduces inflammation (5), and enhances overall well-being.
Combine Extra Virgin Olive Oil with Omega-3 Foods
The Mediterranean diet emphasizes healthy fats from olive oil alongside omega-3 sources like fatty fish, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
For example, you can:
- Drizzle olive oil over roasted salmon or tuna steaks for a flavorful, nutrient-packed meal.
- Mix olive oil with chia seeds in smoothies or breakfast bowls for a dose of ALA omega-3s.
- Toss walnuts into a salad dressed with an olive oil-based vinaigrette.
Replace Unhealthy Fats
Remember, not all fats are created equal. Swap saturated fats like butter or trans fats found in processed foods with olive oil and omega-3-rich options. Use olive oil for cooking or as a dip for whole-grain bread, and opt for meals featuring fish instead of red or processed meats.
Try Omega-3 Supplements with Olive Oil
If your omega-3 intake needs a boost, a liquid fish oil supplement, like Omega Cure, can complement your olive oil recipes. For instance, you can create Anne-Marie’s Dijon and Omega-3 Dressing using:
- 6 tablespoons of extra virgin olive oil
- 2 tablespoons of Omega Cure
- 1/3 cup of balsamic vinegar
- 1 tablespoon of Dijon mustard
- Crushed garlic
Whisk it all together for a delicious way to combine these healthy fats.
Balance is Key
Incorporating olive oil and omega-3-rich foods regularly, while reducing unhealthy fats, ensures a balanced diet that supports long-term health. Plus, these ingredients make every meal more flavorful and satisfying.
Maintain a Balanced Diet Rich in Healthy Fats
Olive oil is undeniably a nutritional superstar. Its rich supply of monounsaturated fats, antioxidants, and polyphenols supports heart health, reduces inflammation, and even offers potential protective benefits against other health conditions. But when it comes to omega-3 fatty acids, olive oil doesn’t quite measure up. With less than 1% ALA omega-3, it’s not a significant source of these essential fats.
To get the best of both worlds, focus on a Mediterranean diet supplemented with both olive oil and omega-3-rich foods. These combinations provide a balance of healthy fats that nourish your body and enhance overall wellness. For an even more effective boost, consider a high-quality omega-3 supplement, such as Omega Cure. Adding it to olive oil-based recipes, like salad dressings or dips, is a simple and tasty way to get the nutrients you need.
A balanced diet that emphasizes healthy fats from diverse sources ensures you reap the full spectrum of benefits—helping you feel great today and supporting your health for years to come.
- Revelou PK, Xagoraris M, Alexandropoulou A, et al. Chemometric Study of Fatty Acid Composition of Virgin Olive Oil from Four Widespread Greek Cultivars. Molecules. 2021;26(14):4151. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144151
- LeWine HE. Is Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Extra Healthy? Harvard Health. Published November 1, 2021.https://www.health.harvard.edu/nutrition/is-extra-virgin-olive-oil-extra-healthy
- Gorzynik-Debicka M, Przychodzen P, Cappello F, et al. Potential Health Benefits of Olive Oil and Plant Polyphenols. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018;19(3):686. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030686
- Gaforio, Visioli, Alarcón-de-la-Lastra, et al. Virgin Olive Oil and Health: Summary of the III International Conference on Virgin Olive Oil and Health Consensus Report, JAEN (Spain) 2018. Nutrients. 2019;11(9):2039. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092039
- Xia M, Zhong Y, Peng Y, Qian C. Olive Oil Consumption and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Frontiers in Nutrition. 2022;9:1041203. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.1041203
- Donat-Vargas C, Lopez-Garcia E, Banegas JR et al. Only Virgin Type of Olive Oil Consumption Reduces the Risk of Mortality. Results from a Mediterranean Population-Based Cohort. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2023;77(2):226-234. doi:10.1038/s41430-022-01221-3
- Cleveland Clinic. Mediterranean Diet. Cleveland Clinic. Published November 20, 2022. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/16037-mediterranean-diet
Popular posts


Related posts