15 Tips for Improving Sleep Habits With and Without Melatonin
When I was young and living with my future in-laws in Norway, my to-be mother-in-law would ask me each morning, “Did you sleep well?”
Being a woman in my early twenties, I remember thinking, “Why is she so concerned about sleep?” As I later found out, my mother-in-law often struggled with sleeping, and the problem progressed as she aged.
Poor Sleeping Habits Troubling You? You’re Not Alone
My mother-in-law’s story is all too common. About 30% of American adults report getting less than seven hours of sleep per night, and approximately 50 to 70 million suffer from chronic sleep disorders. Worryingly, these rates are on the rise and causing havoc with sleepless sufferers.
Poor sleep may related to long work hours, night shifts, technology usage, and chronic illnesses (like obesity and depression). But there is also another factor at play: As we age, the body’s natural production of melatonin decreases after 40. Since melatonin is the prime regulator of our internal “body clock”, this decrease can have a profound impact on not only our sleep, but our daily lives.
Fortunately, there are ways to improve our sleep habits and support our body’s natural production of melatonin. Here are 15 tips for getting some of that elusive shut-eye:
Tip 1: Routine Is Crucial
As boring as it sounds, going to bed at the same time every night and waking up at the same time each morning is one of the simplest and best ways to get better sleep. When you have a regular bedtime, you’ll find that you become tired naturally.
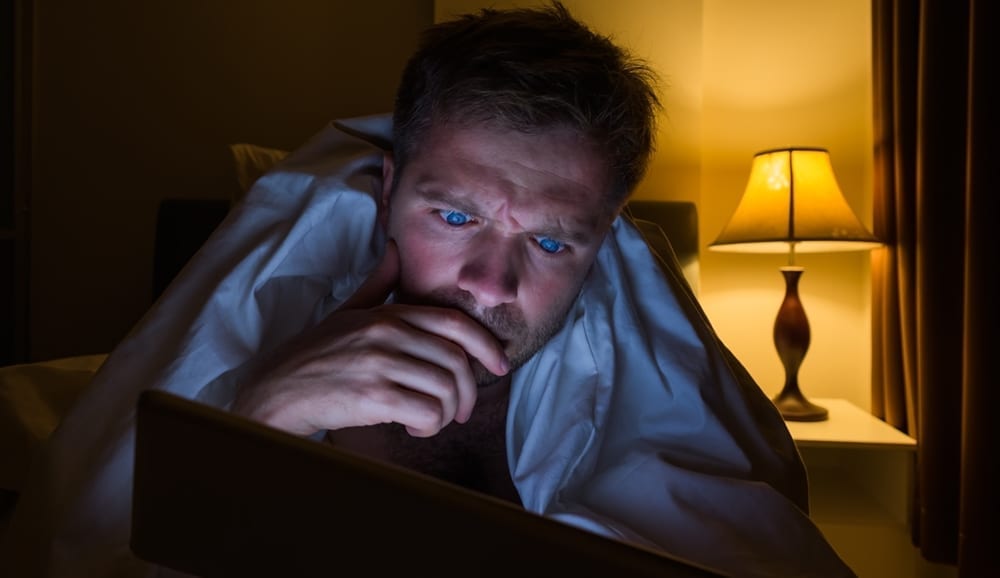
Tip 2. Darken Your Room
The pineal gland secretes melatonin in response to darkness. And unfortunately, light pollution, be it from bedside lamps, laptops, smartphones, and televisions, interferes with the body’s natural production of the hormone. Even just a few seconds of “blue light” exposure can make it harder for you to enter deep sleep.
To stimulate your body’s production of melatonin, set aside your electronic devices before going to bed and turn off all lights. Similarly, avoid checking your devices or turning on any lights if you wake up in the middle of the night. If you find that your bedroom gets too much light from your window, invest in heavy curtains or a sleep mask. You want to keep you sleep surroundings as dark as possible.
To avoid compromising your body’s production of melatonin, turn off electronic devices and lamps.
Tip 3. Get Enough Sunshine
The circadian system – which is partly-controlled by melatonin – responds to both light and dark exposure over a 24-hour period. We highly recommend going outside in the morning and exposing your eyes to sunshine. This “sun break” is a perfect pick-me up.
Tip 4. Avoid Eating Before Bedtime
Avoid heavy meals two to three hours prior to sleeping. Cortisol levels increase while digesting food, which keeps you out of deep sleep. If you normally don’t get home from work until 7 or 8 pm, try flipping your eating pattern so that you eat something more substantial earlier in the day and add a light snack for dinner.
Tip 5. Exercise During the Day
Much like eating late at night, exercise can have a similar effect on cortisol, so aim to get your workout done earlier in the day. Even moderately intense exercise, like brisk walks, can increase the time it takes to fall asleep before bed.
Tip 6. Relax Before Bedtime.
At the end of each day, spend 10 to 20 minutes relaxing. Deep breathing exercises, like the 4-7-8 breathing method, are simple ways to reduce stress (a common culprit that keeps us restless at night).
Tip 7. Move to a New Room
If you’re still wide awake after 30 minutes of trying to sleep, get up and move to another room. Sometimes, finding a change of scenery with a comfortable lounge chair, sofa, or another bed can help.
Tip 8. Use Your Bed for Bed-Related Activities
It’s easy to use your bed to catch up on social media or watch a movie, but you should only associate this space with two things: sex and sleep.
If you wake up feeling like the Princess and the Pea, it might be time to consider replacing your mattress and/or pillows.
Tip 9. Invest in a Better Mattress
An old, lumpy mattress can dramatically affect your sleep cycle. If you wake up with pain or even a runny nose each day, consider purchasing a firmer one that supports your body and provides restful sleep. Even a thicker mattress topper and new pillows can dramatically improve your wake-up routine.
Tip 10. Take a Shower or Bath Before Bedtime
It’s no secret that warm water can have a calming effect on the human body. If you usually shower in the morning, try switching your routine to the evening.
Tip 11. Get Enough Magnesium
Magnesium is a common mineral. When you consume the right amount each day, your parasympathetic nervous system is better able to slow your heart rate, lower blood pressure, and regulate your body’s melatonin production. The recommended daily dose of magnesium for men is around 400mg, while women are recommended to take about 300mg.
Tip 12. Lower Your Room’s Temperature
The human body sleeps best in a room that’s around 65ºF (18.3ºC), and a cooler temperature also boosts melatonin production. Those who suffer from insomnia may have higher core body temperatures than those who don’t, so turning up the AC in summer and cracking a window in colder months may help trigger a better sleep response.
Interestingly enough, melatonin also has a thermoregulatory effect and helps lower the body’s core temperature at night.
Tip 13. Deal with Anxieties in a Healthy Way
Stress and anxiety cause a variety of health problems, and taking them to bed can keep you up at night. Journaling, meditating, or speaking to a professional counselor about chronic concerns may be great options to consider.
Tip 14. Avoid Caffeine and Alcohol
A glass of wine may initially make you sleepy, but alcohol paradoxically acts as a stimulant approximately 3 hours after its ingested. Unsurprisingly, caffeine has a major impact on sleep, and drinking a cup of coffee six hours before bedtime can decrease sleep time by an entire hour!

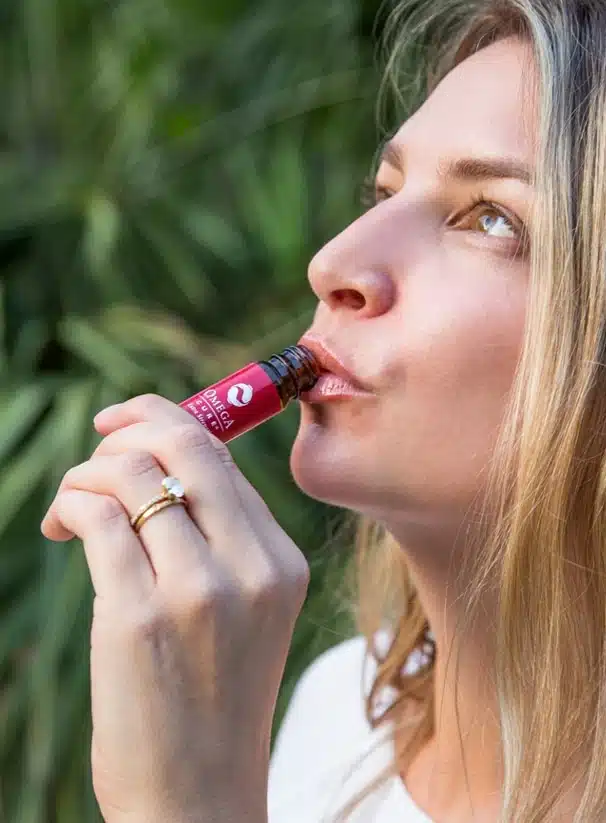
Tip 15. Find a Melatonin Supplement
Many people who have sleep issues may also find it useful to take a melatonin supplement. Melatonin is a sleep regulator, not a sleeping pill. However, some promising research suggests that melatonin supplementation can help improve the sleep quality of people with certain sleep disorders.
Besides being naturally produced by the body, foods high in melatonin include oats, barley, nuts, medicinal herbs, certain types of vegetables and fruits, eggs, and fish. In addition, scientist have also successfully recreated melatonin in the lab – the typical source of the melatonin pills you find at the pharmacy.
After years of research, we’ve also perfected a proprietary blend of long-chain omega-3s combined with melatonin in our Omega Restore fish oil supplement. When these important molecules work together, they appear to help destress the body (among other benefits). Most of our Omega Restore clients remark that they get more restful sleep with a daily vial consumed before bedtime. More importantly, they feel more alert and focused the next day.
Regardless of whether or not your path to better sleep includes taking melatonin, we can all stand to improve our sleep habits by making small changes to our routines. If you have advice to share about how you have improved your sleep habits, leave a comment below. We’ll all be snoozing better for it.
For More Restful Sleep and Energy
Experience the Omega3 Innovations difference for yourself with the most effective fish oil supplement on the market.
Buy Now
Popular posts


Related posts