Can Omega-3 Fish Oil Help Prevent Muscle Wasting?
Muscle wasting. It’s a nasty phenomenon that scares many of us over the age of 40 – especially when we stand naked in front of the mirror!
Known more formally as sarcopenia, muscle wasting is a major issue. As many as 25-45% of older adults in the United States suffer from problematic loss of muscle mass and strength (1). Besides making it harder to carry out everyday physical tasks, sarcopenia is associated with a long list of negative health outcomes, like fractures, hospitalization and early death (2).
While sarcopenia is closely tied to aging, younger adults can suffer from it too. Particularly now with COVID-19 lockdown restrictions making it harder to exercise, sarcopenia is projected to become a larger problem for all age groups (3).
The good news is that there are ways to fight muscle loss, even as we age. In addition to traditional measures – like regular exercise, getting enough protein, and maintaining healthy vitamin D levels – research indicates that omega-3 fatty acids may also be important for preserving our muscle strength.
Does Omega 3 Help with Muscle Growth?
A number of studies have indicated that omega-3s play a role in muscle growth.
Just in the last year, a 2020 study from South Korea found that older women with higher omega-3 levels had a lower risk of sarcopenic obesity (4). In addition, a 2020 meta-analysis of 10 randomized controlled trials found that taking more than 2000 mg of omega-3s daily was associated with a 0.73 pound increase in muscle mass in elderly individuals (2). The same researchers also found that taking omega-3 supplements improved walking speed when the participants received the omega-3 supplements for more than 6 months.
While such improvements may seem minor to the Arnold Schwarzenegger bodybuilders among us, keep in mind that most people after age 50 lose 2% of their muscle mass on a yearly basis (5). Thus, even small improvements in muscle mass and mobility can be meaningful.
These 2020 findings importantly reiterate the results from previous trials. Consider one 2015 study, which found that giving healthy older individuals 3360 mg of EPA/DHA omega-3s daily for 6 months increased thigh muscle volume, handgrip strength, and one-repetition muscle strength (compared to the control group). The researchers of this study noted that, in functional terms, taking the omega-3 supplements had prevented 2 – 3 years worth of normal age-associated losses in muscle mass and function (6).
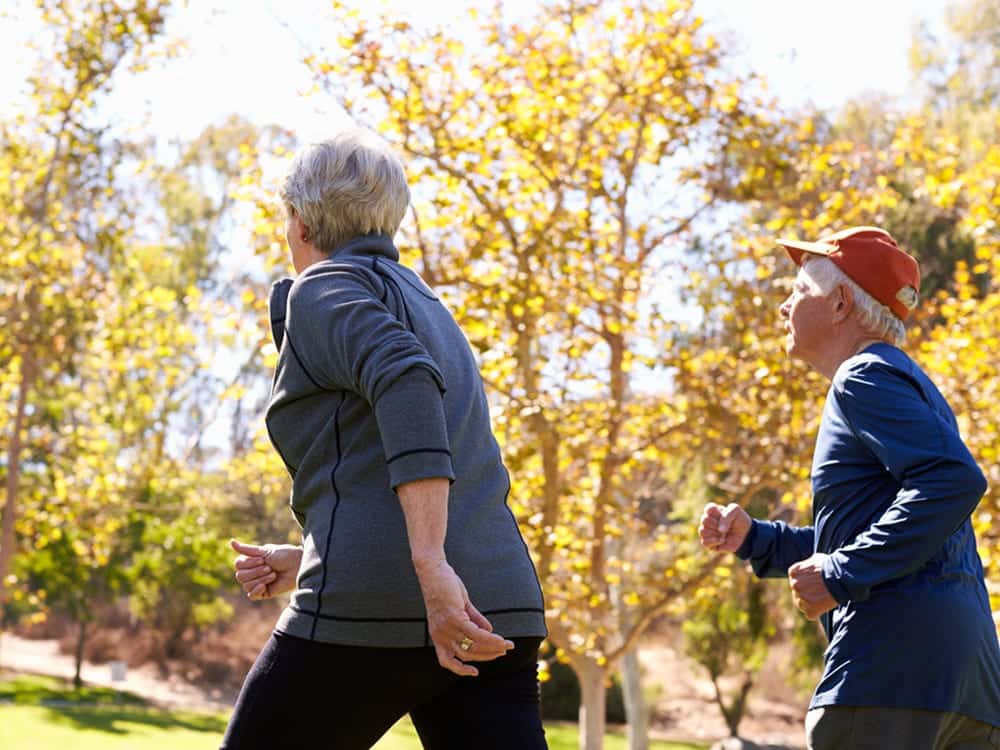

In a 2020 meta-analysis of 10 randomized controlled trials, researchers found that supplementing with at least 2000 mg of omega-3s for more than 6 months improved walking speed (one of the tools for measuring sarcopenia).
Why Does Fish Oil Help Build Muscle?
Scientists are still working to understand exactly how omega-3s influence muscle mass. But sarcopenia researchers have some educated ideas as to why these important fatty acids make a difference:
Omega-3s Fight Chronic Inflammation
One of the central theories is that omega-3s help fight a phenomenon known as “inflammaging,” which is age-related chronic low-grade inflammation. With inflammaging, the body produces higher levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines that affect signaling pathways for muscle anabolism (ie. muscle building) and catabolism (ie. muscle breakdown).
Since omega-3s have been shown to reduce high levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, they may help resolve destructive ongoing inflammation and make the body more effective at building muscle (7, 8).
Omega-3s Reduce Oxidative Stress
Another mechanism could be that omega-3s support muscle mass by counteracting the damage of oxidative stress. Oxidative stress – which is generally caused by poor eating habits, inactivity, smoking, pollution, etc. – contributes to sarcopenia by decreasing muscle protein synthesis. Over time, prolonged oxidative stress can reduce muscle mass quantity (9).
During intense bouts of exercise, the body produces free radicals as a normal part of cell metabolism. Typically, the body is able to combat these free radicals during exercise by increasing its antioxidant production. However, if the body produces more free radicals than the muscles are able to handle, oxidative stress can occur (10). Promisingly, omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to reduce certain oxidative stress markers both after exercise and generally too (11, 12).

While regular exercise is crucial for building muscle, intense exercise like marathon running can increase oxidative stress.
Omega-3s May Fight Anabolic Resistance
Part of what makes these theories especially exciting is that they could help address one of the biggest challenges with sarcopenia: Anabolic resistance.
Anabolic resistance refers to the body’s reduced ability to build muscle, even when getting enough exercise, amino acids, protein, etc. Since anabolic resistance increases with age, some researchers believe that adding omega-3s to the mix could be key to achieving better exercise results in older individuals (4).
How Much Omega-3 Do You Need Every Day?
One of the tricky things about the current omega-3 literature on muscle building is that the trials use a variety of EPA/DHA dosages, supplement sources, exercise protocols, and other variables. Therefore, the findings are not always straightforward or conclusive.
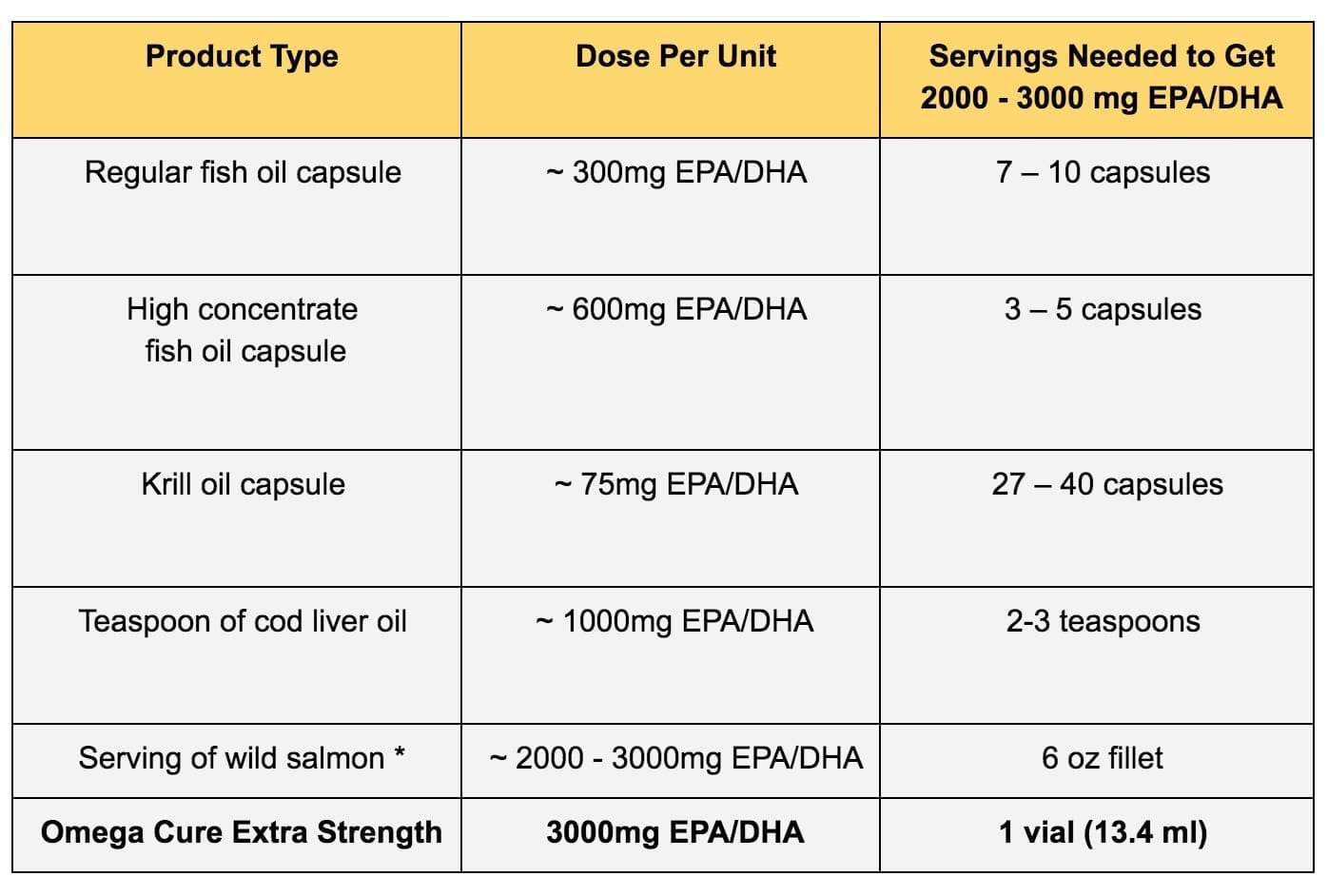
With that said, several reviews have identified that getting at least 3000 mg of EPA/DHA omega-3s daily may be necessary in order to achieve positive results for muscle mass and strength in older adults (13, 14). Since most fish oil capsules contain just 10% of that amount (approximately 300 mg of EPA/DHA per gel cap), this dosage can be hard to replicate through regular omega-3 supplements.
For easier-to-swallow alternatives to fish oil capsules, liquid Omega Cure® Extra Strength and Omega Restore provide 3000 mg of EPA/DHA in pre-measured vials. That’s roughly the same amount of omega-3s found in a 6oz. fillet of wild-caught salmon – but without any fishy smell or taste.
* Regular fish oil supplements typically contain just 300 mg of EPA/DHA per gel capsule, although dosages vary between products. The omega-3 content of salmon similarly varies depending on the species, cooking method, etc.
Omega-3s Are Just Part of the Solution
With this discussion, keep in mind that omega-3s are just part of the picture. There are many elements that work in synchronicity when it comes to supporting good muscle health.
Find Exercise That Motivates You
First of all, regular exercise – particularly resistance training – is the most important tool to fighting muscle loss (5). And just because you’re older doesn’t mean that it’s too late to start: Many people – including bodybuilding grandmother Ernestine Shepherd and Richard Becker – have transformed their muscles later in life.
Get the Right Nutrients
While getting enough omega-3 fish oil every day is great, there are other nutrients to consider, too. When it comes to fighting oxidative stress and inflammation, there’s exciting research on antioxidants like melatonin (although melatonin and sarcopenia clinical studies are still in the early stages) (15). Then, of course, there are the old nutritional stalwarts, like proteins, vitamin D, and certain amino acids (14, 16).
For Best Results, Try a Synergistic Approach
As several reviews have outlined, combining these varied interventions will likely produce better results than attempting just one (7, 14). Such a multi-pronged perspective has always made sense to us here at Omega3 Innovations. That is why we take a synergistic approach in creating our products – such as combining our pristine omega-3 oil together with vitamin D3 and melatonin.
In short, there is hope for your muscles after age 40. With the right nutrients and consistent exercise, you can work to preserve and increase your muscle strength. With time, looking in the mirror will be a less frightful experience!
For More Restful Sleep and Energy
Experience the Omega3 Innovations difference for yourself with the most effective fish oil supplement on the market.
Buy Now
References:
1. Du, K., Goates, S., Arensberg, M. B., Pereira, S. & Gaillard, T. (2018). Prevalence of Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity Vary with Race/Ethnicity and Advancing Age. Diversity and Equality in Health and Care (2018) 15(4): 175-183.
2. Huang, Y. H., Chiu, W. C., Hsu, Y. P., Lo, Y. L. & Wang, Y. H. (2020). Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Muscle Mass, Muscle Strength and Muscle Performance among the Elderly: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 12(12), 3739.
3. Kirwan, R., McCullough, D., Butler, T., Perez de Heredia, F., Davies, I. G. & Stewart, C. (2020). Sarcopenia During COVID-19 Lockdown Restrictions: Long-Term Health Effects of Short-Term Muscle Loss. GeroScience, 42(6): 1547–1578.
4. Yang, W., Lee, J. W., Kim, Y., Lee, J. H. & Kang, H. T. (2020). Increased Omega-3 Fatty Acid Intake Is Inversely Associated with Sarcopenic Obesity in Women But Not in Men, Based on the 2014-2018 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(12), 3856.
5. Papa, E. V., Dong, X. & Hassan, M. (2017). Resistance Training for Activity Limitations in Older Adults with Skeletal Muscle Function Deficits: A Systematic Review. Clinical Interventions in Aging, 12, 955–961.
6. Smith, G. I., Julliand, S., Reeds, D. N., Sinacore, D. R., Klein, S. & Mittendorfer, B. (2015). Fish Oil-Derived N-3 PUFA Therapy Increases Muscle Mass and Function in Healthy Older Adults. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 102(1), 115–122.
7. Dupont, J., Dedeyne, L., Dalle, S., Koppo, K. & Gielen, E. (2019). The Role of Omega-3 in the Prevention and Treatment of Sarcopenia. Aging Clinical and Experimental Research, 31(6), 825–836.
8. 13. McGlory, C., Calder, P. C. & Nunes, E. A. (2019). The Influence of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Skeletal Muscle Protein Turnover in Health, Disuse, and Disease. Frontiers in Nutrition, 6, 144
9. Liguori, I., Russo, G., Curcio, F., Bulli, G., Aran, L., Della-Morte, D., Gargiulo, G., Testa, G., Cacciatore, F., Bonaduce, D. & Abete, P. (2018). Oxidative Stress, Aging, and Diseases. Clinical Interventions in Aging, 13, 757–772.
10. Gammone, M. A., Riccioni, G., Parrinello, G. & D’Orazio, N. (2018). Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: Benefits and Endpoints in Sport. Nutrients, 11(1), 46.
11. Heshmati, J., Morvaridzadeh, M., Maroufizadeh, S., Akbari, A., Yavari, M., Amirinejad, A., Maleki-Hajiagha, A. & Sepidarkish, M. (2019). Omega-3 Fatty Acids Supplementation and Oxidative Stress Parameters: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. Pharmacological Research, 149:104462.
12. de Salazar, L., Torregrosa-García, A., Luque-Rubia, A. J., Ávila-Gandía, V., Domingo, J. C. & López-Román, F. J. (2020). Oxidative Stress in Endurance Cycling Is Reduced Dose-Dependently after One Month of Re-Esterified DHA Supplementation. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland), 9(11), 1145.
13. Troesch, B., Eggersdorfer, M., Laviano, A., Rolland, Y., Smith, A. D., Warnke, I., Weimann, A. & Calder, P. C. (2020). Expert Opinion on Benefits of Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acids (DHA and EPA) in Aging and Clinical Nutrition. Nutrients, 12(9), 2555.
14. Tessier, A. J. & Chevalier, S. (2018). An Update on Protein, Leucine, Omega-3 Fatty Acids, and Vitamin D in the Prevention and Treatment of Sarcopenia and Functional Decline. Nutrients, 10(8), 1099.
15. Stacchiotti, A., Favero, G. & Rodella, L. F. (2020). Impact of Melatonin on Skeletal Muscle and Exercise. Cells, 9(2), 288.
16. Ganapathy, A. & Nieves, J. W. (2020). Nutrition and Sarcopenia-What Do We Know? Nutrients, 12(6), 1755.
Popular posts


Related posts