Should I Take Omega 3 Fish Oil for Fertility?
As a public health nurse in the 1960s, my mother cared for many unwed, pregnant teenagers. As I was growing up, she gave me the impression that “just looking at a boy” would land me in the same boat.
My attitude changed in medical school while I was working at a fertility clinic. During this time, I discovered my mother may have been exaggerating, just a bit, as I saw many couples struggling to have children.
Indeed, infertility affects about 15% of couples worldwide [1]. Moreover, that number is on the rise [2].
For those hoping to conceive, reading the dismal statistics about declining sperm counts and increasing miscarriage rates can be alarming. But there is also good news to note! Clinical studies find promising links between omega-3 and fertility in both men and women.
Omega 3 and Female Fertility
Omega-3s – those beneficial fats found plentifully in fish – appear helpful for a variety of female fertility issues.
Age-Related Fertility Issues
As women are reminded all too often, fertility decreases through one’s 30s. By age 40, a woman has just a 5% chance of getting pregnant each month, compared to the 20% chance of her 30-year-old counterpart [3].
With more women waiting to have children, a number of studies have examined how omega-3s impact age-related fertility issues.
One 2012 study on mice concluded that consistently eating a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids could extend reproductive function into advanced maternal age. The researchers also found that even a short-term omega-3 regimen could improve egg (oocyte) quality [4].
Multitasking fatty acids: Omega-3s play many roles in our bodies, from reducing inflammation to regulating gene expression. No wonder they’re vital for both conception and a healthy pregnancy!
Human studies have found similar trends when looking at the relationship between omega-3s and the follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). As women approach menopause, their FSH levels increase. For that reason, high FSH levels are usually seen as a sign of ovarian aging.
In a 2016 study, researchers found that taking 4000 mg of EPA/DHA omega-3s decreased FSH levels in normal weight women [5]. In 2019, the researchers replicated their findings with a new group of women and the same omega-3 dosage. Again, they found the omega-3s decreased the women’s FSH levels by almost 30% [6].
Sadly, in both studies, the benefits did not extend to overweight women. However, the findings indicate that higher intakes of omega-3s may help normal weight women conceive later in life.
Omega-3s and Inflammatory Reproductive Issues
Omega-3s may also lessen inflammation-related fertility problems.
One 2015 study looked at the relationship between endometriosis and the omega-3 levels of women undergoing IVF. The women with high blood levels of EPA omega-3 were 82% less likely to have endometriosis compared to the women with low EPA levels [7]. In animal models, researchers have also found that omega-3s can suppress endometriosis lesions [7].
Separately, research suggests omega-3s may lessen ovarian dysfunction caused by high fat diets. In a 2021 animal study, researchers found that DHA omega-3 improved certain aspects of ovarian function by reducing macrophage infiltration [8].
Omega-3 Fish Oil & Preterm Delivery
After conception, omega-3 fatty acids continue to play a crucial role. Numerous studies show that getting enough omega-3s reduces the risk of early preterm delivery, one of the leading causes of infant mortality [9].
For instance, one Danish survey found that, in high-risk pregnant women who didn’t eat seafood or take an omega-3 supplement, the premature birth rate was 7.1%. For those who did eat fish regularly, the rate was just 1.9% [10].
Similarly, a 2018 study found that women with higher omega-3 levels had better odds of both clinical pregnancy and live birth when undergoing assisted reproduction. In fact, for every 1% increase in omega-3 levels, the chances of getting pregnant and giving birth increased by 8% [11].
Healthy swimmers: Consuming more omega-3s is linked with improved sperm motility.
The Relationship Between Fish Oil and Male Fertility
I’ve often joked that there should be a warning label on Omega Cure®, cautioning men that omega-3s may increase their sperm’s vigor. And when you look at the research, there’s plenty of scientific basis for my admonishment.
Sperm contains higher concentrations of DHA compared to other cells, suggesting that this omega 3 fatty acid is important for the viability, maturity, and performance of those little swimmers [12].
Further studies have determined that higher omega-3s levels correlate with improved sperm count, morphology, and motility [13, 1]. In other words, there’s more sperm, they’re more robust – and they swim faster. Tell that ovum to watch out!
Does Omega 3 Help Male Infertility?
While high levels of omega-3s correlate with improved sperm metrics, scientists have wondered if supplementation directly impacts male fertility. Fortunately, the research looks promising.
In a 2019 meta-analysis analysis of 16 randomized, controlled trials, the researchers showed a positive relationship between omega-3 supplementation and semen quality in infertile men [1].
Another smaller study found that a 3-month intervention of omega-3s plus other vitamins significantly reduced harmful DFI levels in infertile participants [14]. That’s important, since high DFI levels (or the amount of sperm DNA fragmentation) is a male infertility indicator.

How to get enough omega-3s: Eating fish and taking a good quality supplement are the two best ways to increase your intake of EPA and DHA. EPA and DHA are the most important omegas for fertility.
Omega 3 for Fertility Dosage
While science highlights the benefits of omega-3s, the question remains: How much do we actually need to increase the odds of conception?
Ultimately, optimal dosage depends on a person’s age, body weight, genetics, lifestyle and overall health condition. However, the unfortunate reality is that many men and women don’t get enough omega-3s from their daily diet.
Only 19% of Americans eat the recommended 2 servings of fish per week [10]. Furthermore, an estimated 95% of Americans have low omega-3 levels [15].
How to Increase Your Omega-3 Levels
While there are different types of omega-3s, the most important ones for fertility are called EPA and DHA. To get a meaningful amount of these long-chain fatty acids, you really only have two options: Eating fish or supplementing.
Eating fatty fish (like salmon, herring and sardines) is a great way to increase your EPA and DHA levels. And regularly putting fish on the menu has a good track record! In a 2018 study, couples who consumed eight or more seafood servings per ovulation cycle had 47% and 60% greater conception success than couples who consumed one or fewer seafood servings per cycle [16].
Capsules vs. Liquid Fish Oil
In many successful trials, however, scientists use omega-3 doses that can be challenging to achieve through diet alone. In looking at the impact of omega-3s on ovarian function, the researchers explained that a person would have to take between 3000 – 4900 mg of DHA to mimic the doses given to the test animals [8].
To get higher omega-3 doses, fish oil supplements may be necessary for many individuals. However, before you run to the local pharmacy, it’s important to consider the delivery method first.
Before picking an omega-3 supplement, make sure to check the amount of EPA and DHA it provides per serving. Regular fish oil capsules tend to contain only 10-15% of the omega-3s used in successful clinical trials.
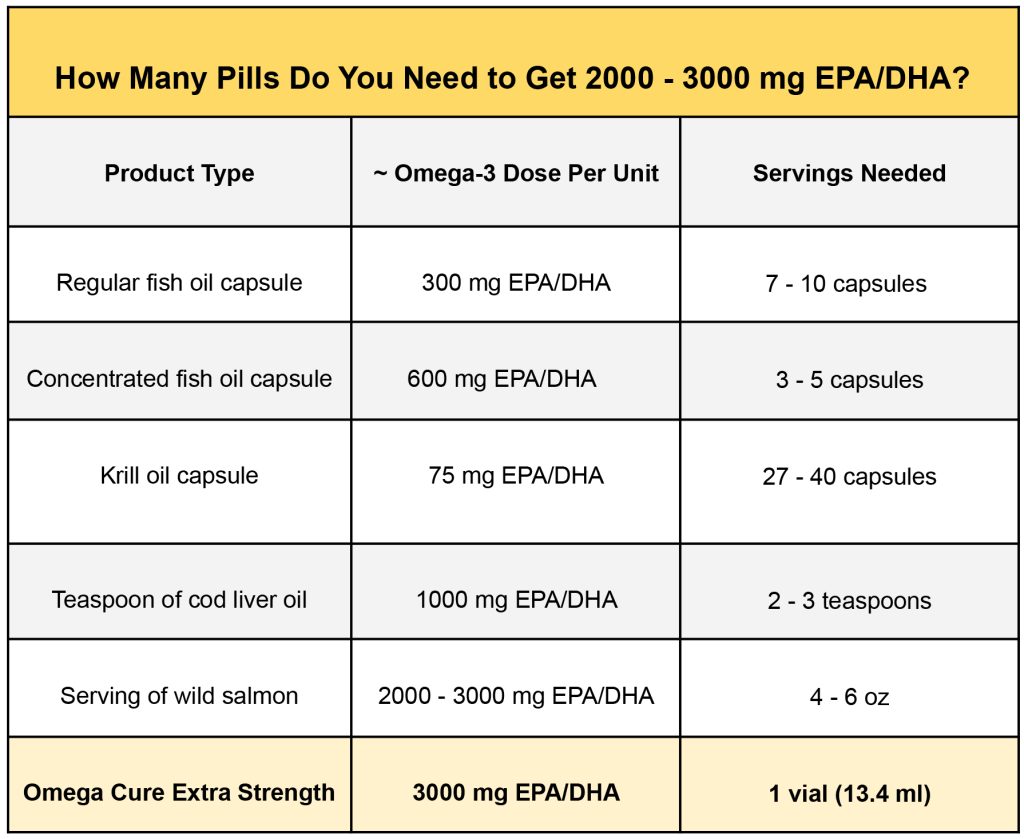
Smarter dosing: Liquid fish oils, like Omega Cure Extra Strength, usually make it easier to get an effective omega-3 dose than popping a handful of pills.
Full-Spectrum Fish Oil Matters, Too
When choosing a supplement, it’s also important to consider what type of omega-3s your product contains. Many prenatal supplements only provide DHA.
While getting enough DHA is a step in the right direction, you don’t want to neglect the other members of the omega-3 family. Many newer studies indicate that EPA may play a bigger role in inflammation-driven fertility issues [7, 11].
Additionally, DHA depends on EPA to help carry it across the placenta and into the fetus [10].
Prenatal Fish Oil Supplements Are Often Rancid
I’d also be remiss if I didn’t mention fish oil rancidity. Studies from across the globe have discovered that many omega-3 supplements exceed acceptable oxidation limits before their stated expiration dates [17, 18].
Let’s phrase it this way: You wouldn’t eat salmon that’s stored at room temperature for two years, would you? Rancid fish oil isn’t beneficial for anyone – and may even have negative health effects.
Choose the Best Omega-3 Supplement for Fertility
Thinking about my mother, I smile when I remember what she taught me about sex growing up. Certainly, omega-3s did not make the lesson plan back then.
In later years though, she undoubtedly would have been excited to discover how these fatty acids support fertility and healthy pregnancy. Always interested in quality, I’m sure she also would have been interested in how dose and freshness impact omega-3 benefits.
For those who are curious, a single serving of our liquid fish oil provides 3000 mg of full-spectrum omega-3s. Omega Cure Extra Strength also ensures that you’re also getting the freshest fish oil on the market (with certified low oxidation levels).
Regardless of the product you choose, however, I hope that this information will be helpful to anyone hoping to expand their family.
Try Exceptionally Fresh Omega Cure
Experience the Omega3 Innovations difference for yourself with the most effective fish oil supplement on the market.
Buy Now
- Skoracka, K., Eder, P., Łykowska-Szuber, L., Dobrowolska, A., & Krela-Kaźmierczak, I. (2020). Diet and Nutritional Factors in Male (In)fertility-Underestimated Factors. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(5), 1400.
- Swan, S. H. & Colino, S. (2021, March 16). Reproductive Problems in Both Men and Women Are Rising at an Alarming Rate. Scientific American.
- Age & Fertility: A Guide for Patients. (2012). American Society for Reproductive Medicine.
- Nehra, D., Le, H. D., Fallon, E. M., Carlson, S. J., Woods, D., White, Y. A., et al. (2012). Prolonging the Female Reproductive Lifespan and Improving Egg Quality with Dietary Omega-3 Fatty Acids. Aging Cell, 11(6), 1046–1054.
- Al-Safi, Z. A., Liu, H., Carlson, N. E., Chosich, J., Harris, M., Bradford, A. P., Robledo, C., Eckel, R. H., & Polotsky, A. J. (2016). Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation Lowers Serum FSH in Normal Weight But Not Obese Women. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 101(1), 324–333.
- Bauer, J. L., Kuhn, K., Bradford, A. P., Al-Safi, Z. A., Harris, M. A., Eckel, R. H., Robledo, C. Y., et al. (2019). Reduction in FSH Throughout the Menstrual Cycle After Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation in Young Normal Weight But Not Obese Women. Reproductive Sciences (Thousand Oaks, Calif.), 26(8), 1025–1033.
- Hopeman, M. M., Riley, J. K., Frolova, A. I., Jiang, H., & Jungheim, E. S. (2015). Serum Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Endometriosis. Reproductive Sciences (Thousand Oaks, Calif.), 22(9), 1083–1087.
- Hohos, N. M., Elliott, E. M., Cho, K. J., Lin, I. S., Rudolph, M. C., & Skaznik-Wikiel, M. E. (2020). High-Fat Diet-Induced Dysregulation of Ovarian Gene Expression Is Restored with Chronic Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 499, 110615.
- Kar, S., Wong, M., Rogozinska, E., & Thangaratinam, S. (2016). Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Prevention of Early Preterm Delivery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Studies. European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology, 198:40-46.
- Greenberg, J. A., Bell, S. J., & Ausdal, W. V. (2008). Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation During Pregnancy. Reviews in Obstetrics & Gynecology, 1(4), 162–169.
- Chiu, Y. H., Karmon, A. E., Gaskins, A. J., Arvizu, M., Williams, P. L., Souter, I., Rueda, B. R., Hauser, R., Chavarro, J. E., & EARTH Study Team (2018). Serum Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Treatment Outcomes Among Women Undergoing Assisted Reproduction. Human Reproduction (Oxford, England), 33(1), 156–165.
- Esmaeili, V., Shahverdi, A.H., Moghadasian, M.H., & Alizadeh, A.R. (2015). Dietary Fatty Acids Affect Semen Quality: A Review. Andrology, 3: 450-461
- Salas-Huetos, A., Rosique-Esteban, N., Becerra-Tomás, N., Vizmanos, B., Bulló, M., & Salas-Salvadó, J. (2018). The Effect of Nutrients and Dietary Supplements on Sperm Quality Parameters: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Advances in Nutrition (Bethesda, Md.), 9(6), 833–848.
- Humaidan, P., Haahr, T., Povlsen, B. B., et al. (2021). The Combined Effect of Lifestyle Intervention and Antioxidant Therapy on Sperm DNA Fragmentation and Seminal Oxidative Stress in IVF Patients: A Pilot Study. International Brazilian Journal of Urology, 47.
- Daniells, S. (2015, December 10). Could Widespread Low Omega-3 Levels Be Putting American Hearts at Risk? Nutra-Ingredients-USA.
- Gaskins, A. J., Sundaram, R., Buck Louis, G. M., & Chavarro, J. E. (2018). Seafood Intake, Sexual Activity, and Time to Pregnancy. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 103(7), 2680–2688.
- Jackowski, S. A., Alvi, A. Z., Mirajkar, A., Imani, Z., Gamalevych, Y., Shaikh, N. A., & Jackowski, G. (2015). Oxidation Levels of North American Over-the-Counter N-3 (Omega-3) Supplements and the Influence of Supplement Formulation and Delivery Form on Evaluating Oxidative Safety. Journal of Nutritional Science, 4, e30.
- Wang, W., Yang, H., Johnson, D., Gensler, C., Decker, E., & Zhang, G. (2017). Chemistry and Biology of ω-3 PUFA Peroxidation-Derived Compounds. Prostaglandins & Other Lipid Mediators, 132, 84-91.
Popular posts


Related posts