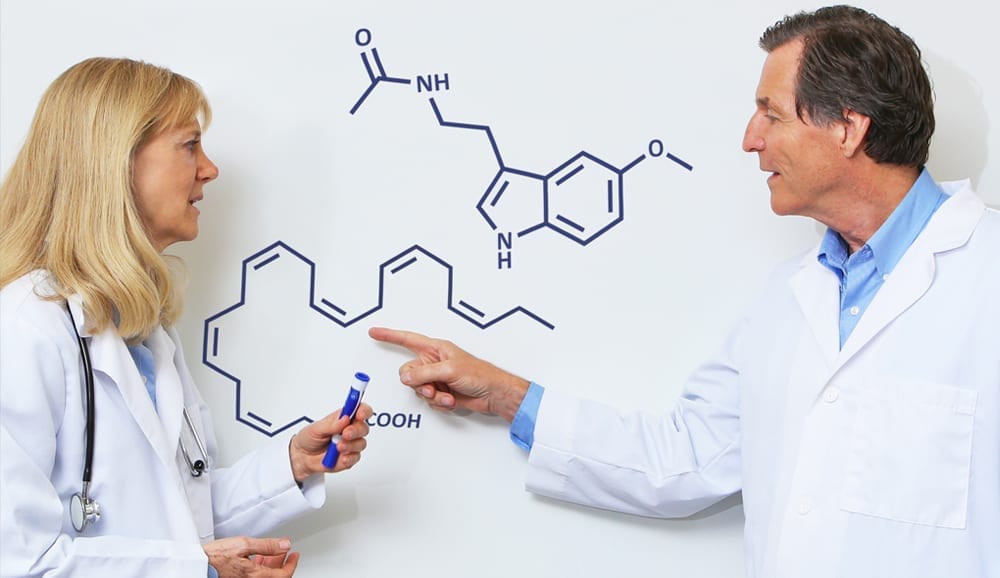
Omega-3 & Melatonin: Not Just for Better Sleep
“I don’t need melatonin – I sleep like a log.”
That’s what many say when they hear about Omega Restore (a combination of omega-3s, vitamin D3, and melatonin).
It’s true that melatonin influences our sleep and helps regulate our circadian rhythm. But melatonin’s effects extend far beyond getting a good night’s rest.
Today, melatonin is getting attention in cancer medicine, as well as for many brain and eye issues. In addition, here at Omega3 Innovations, we’re excited about how this natural hormone potentiates fish oil benefits.
Let’s take a closer look at the advantages of melatonin, and why it makes an excellent partner to your omega-3 oil.
Melatonin’s Incredible Relationship with Omega-3s
Melatonin’s primordial function had nothing to do with sleep. Around 3 billion years ago, bacteria started synthesizing this ancient molecule as an antioxidant to protect against free radicals [1].
This antioxidant benefit impacts human health, too. Chronically high levels of free radicals – whether coming from fried foods, alcohol, smoking, UV-radiation, pollution, or other nefarious sources – can damage cells. If unchecked by enough antioxidants, free radicals overwhelm the body and create oxidative stress. Oxidative stress, in turn, fuels many common diseases.
Melatonin’s antioxidant properties make it a promising antidote for many conditions exacerbated by oxidative stress, and the applications don’t stop there!
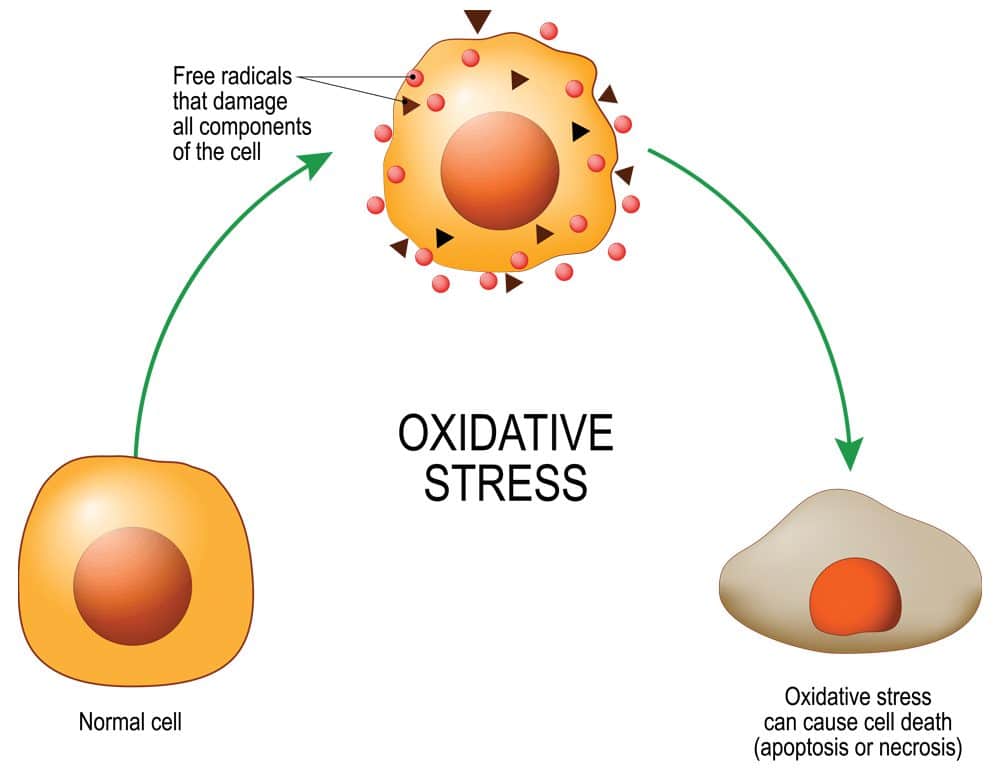
Protecting against free radicals: Due to its antioxidant effect, melatonin (together with omega-3s) can be a helpful tool in the fight against oxidative stress.
May Protect Omega-3s
Long-chained omega-3 fatty acids are characterized by multiple double bonds, which give them their unique flexibility. However, these double bonds also make omega-3s susceptible to free radicals.
When the omega-3 molecule encounters free radicals, the fatty acid is destabilized, causing it to oxidize. As it oxidizes, the omega-3 molecule loses potency and releases new byproducts that smell and taste bad.
One of the primary ways to protect an omega-3 oil from oxidizing is to add antioxidants – and that’s exactly where melatonin comes in!
Melatonin has been shown to be more powerful than popular antioxidants like vitamin C and E [2, 3]. Plus, one study found that adding certain concentrations of melatonin almost completely halted the lipid peroxidation of omega-3 molecules [4].
May Increase Omega-3 Levels
Melatonin may also promote the absorption of certain types of omega-3s. In one rat study, researchers found that melatonin increased EPA levels by 43-60%, thereby restoring the ratio of EPA to arachidonic acid (AA) [5].
This is vital because the EPA:AA ratio indicates the level of inflammation in the body. It’s also a strong predictor of heart disease, cancer, and other health issues [6, 7].
While more research is needed, this study does reflect a trend we’ve noticed amongst our customers: Omega Restore users typically report higher omega-3 index levels than those taking our signature omega-3 oil by itself.
Omega-3s Also Affect Melatonin
This is not just a one-sided relationship, though: Numerous studies suggest that melatonin also benefits from its interaction with omega-3s.
May Regulate Melatonin Synthesis
The pineal gland is the part of the brain responsible for secreting melatonin at night. Intriguingly, the omega-3 fatty acid DHA makes up a big portion of the fats in this gland. For that reason, some scientists believe the pineal gland may be synergistically regulated by omega-3s [8].
One study found omega-3-deficient hamsters had a 52% lower level of melatonin at night compared to the control group [9]. Furthermore, a 2021 meta-analysis determined that children with higher omega-3 levels had fewer sleep disturbances [10]. And a study of healthy adults aged 25 – 49 showed fish oil supplementation improved sleep efficiency [11].
While more research is needed on the relationship between fish oil and sleep, these studies support the theory that omega-3s may influence our melatonin synthesis.
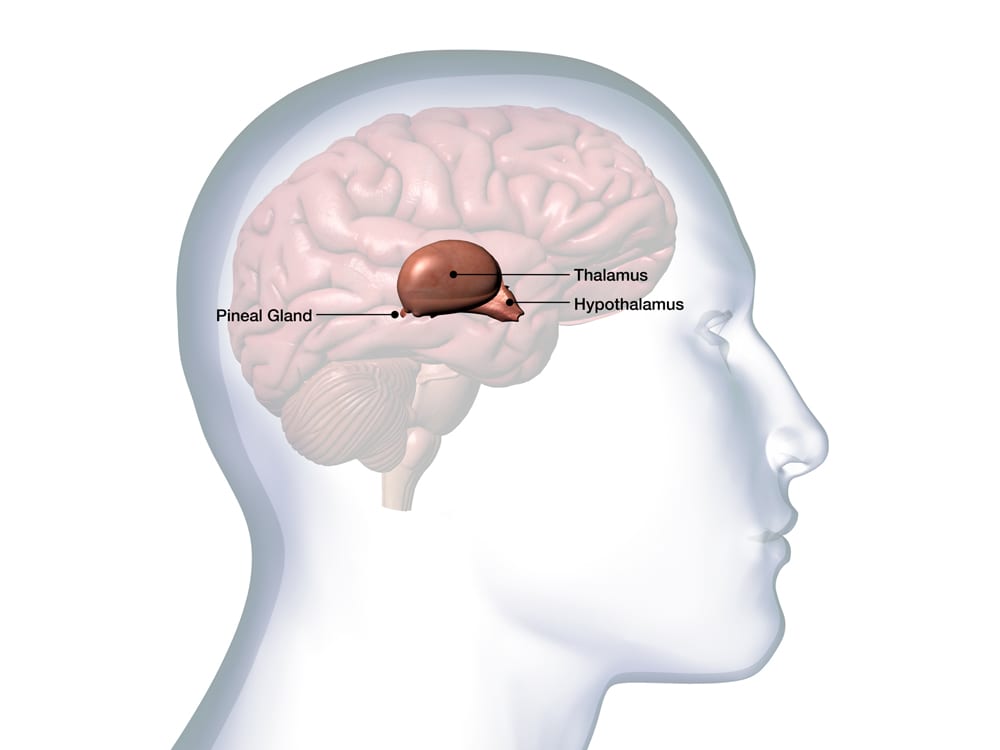
Does fish oil help you sleep better? While scientists can’t answer that question yet, omega-3s do make up a big portion of the fats in the pineal gland. That’s exciting since the pineal gland is the main producer of melatonin for sleep.
Omega 3 and Melatonin’s Synergistic Benefits
Melatonin and omega-3s also complement each other on multiple health fronts:
Fight Inflammation
Take inflammation, for instance. Both omega-3s and melatonin inhibit the production of certain pro-inflammatory cytokines, like IL-6.
These nutrients also have independent ways of fighting inflammation. EPA and DHA, for example, give rise to specialized pro-resolving mediators, which are deeply involved in healing the body from inflammation and disease [12]. Meanwhile, melatonin inhibits a host of inflammation-driving signals and reduces inflammation through its antioxidant properties [13, 14].
Improve Cell Signaling
Omega-3s facilitate signals between cells and different organelles within the cell.
If our cells aren’t signaling properly, we don’t function well. For instance, a lack of omega-3s is linked with decreased learning ability and focus – most likely due to poor cell signaling in the brain [15, 16].
Melatonin allows omega-3s to have greater mobility within the cell membrane, which further improves the transmission of cell signals. Think of it as behaving similarly to when you move around your home to get better reception for your cell phone signal.
What Health and Wellness Studies Say About Omega-3s and Melatonin
While melatonin and omega-3s have synergistic effects, there aren’t many clinical trials using them simultaneously. That’s because in research, scientists tend to work with just one substance at a time.
In the future, however, there’ll likely be more studies examining this potent combination – particularly in the health areas below:
1. Cancer
For the past 30 years, melatonin has shown incredible promise for slowing the spread and growth of cancer tumors. The hormone has also been named as a good adjunct to chemotherapy and radiation therapy – especially for endocrine-responsive tumors [17, 18, 19]. Since melatonin is usually well tolerated with no toxicity, a number of studies recommend using it in cancer prevention and treatment.
With regards to omega-3s, cell and animal studies have confirmed that DHA can inhibit tumor growth [20]. Long-term omega-3 intake is also associated with a reduced risk of certain cancers (like breast and colorectal). In trials, however, results have been mixed.
When it comes to cancer treatment, omega-3s are commonly prescribed for cachexia, a condition that occurs when patients lose substantial weight and muscle mass. Researchers are also exploring how omega-3s influence other cancer complications, like pain and depression [21].
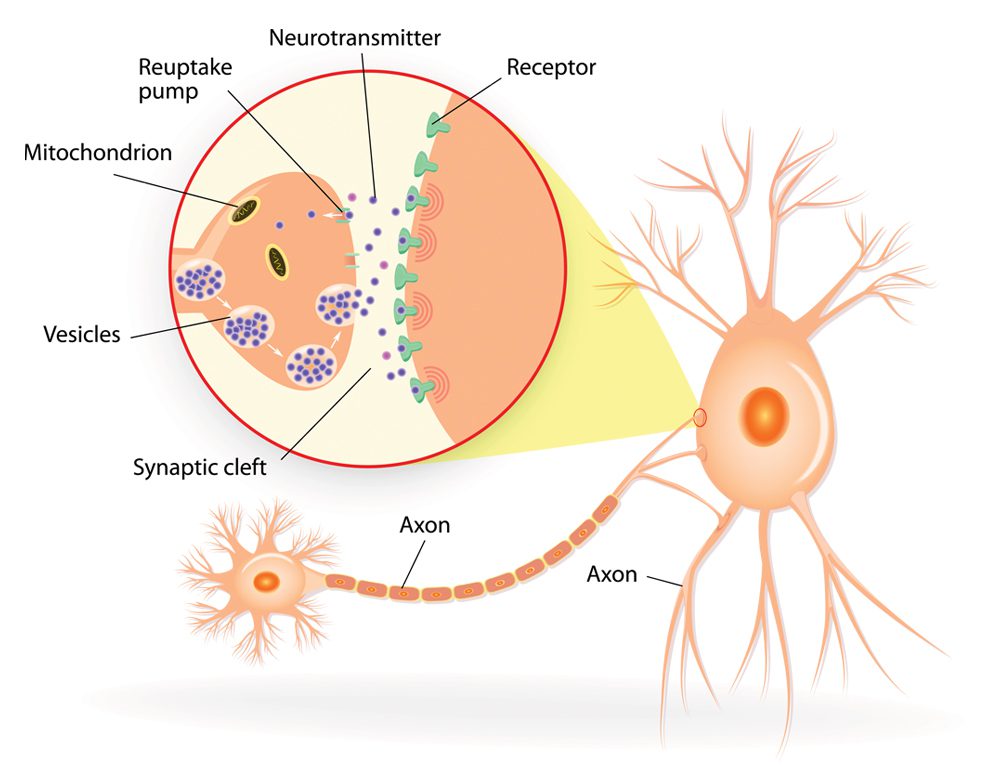
Omega-3s on the brain: Omega-3s influence our cell signaling. That’s especially important in the brain, where these fatty acids facilitate neurotransmission (vital for learning, mood, and more).
2. Brain Heath
Compared to other organs, the brain is made up of lots of fatty acids and consumes lots of oxygen. Hence, it’s especially vulnerable to oxidative stress and the neurodegenerative diseases that follow.
With its antioxidant benefit, melatonin may support patients with Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and traumatic brain injuries, although more research is needed [22].
Omega-3s also play an important role in the brain. DHA comprises about 3% of the dry weight of the cerebral cortex. And, since omega-3s promote healthy cell signaling, we need enough of these fatty acids to support the brain’s 80 billion neurons. Sadly, in both animal and human studies, omega-3 deficient diets have been linked with reduced neurotransmission, as well as increased aggression and depression [23].
Like with melatonin, scientists have long speculated that omega-3s’ may benefit Alzheimer’s disease patients. However, human trials have been mixed, so more studies are necessary.
3. Eye Health
These two nutrients are also crucial for healthy eyes.
Melatonin is synthesized in the eye at night and appears to regulate dopamine release (important for eye movement and pupil activity), intraocular pressure control, and more. Studies also show that people with eye diseases often have a dysregulated circadian rhythm, indicating they’re not producing enough melatonin [24].
As for omega-3s, DHA comprises some 50-70% of the fatty acids in certain segments of the retina and is essential for optimal visual functioning [25]. As with melatonin, people with dry eyes, glaucoma and other eye issues are typically deficient in omega-3s, too. One study determined a 30% reduced risk for dry eye disease with each additional 1000 mg of omega-3 consumed daily [26]!
Is Omega Restore Right for Me?
Because of its synergistic ingredients, we consider Omega Restore our most potent product. However, it’s not for everyone.
We usually only suggest it to customers over the age of 40, which is when the body’s production of melatonin has typically substantially decreased [27]. With that said, melatonin supplements can sometimes be useful for those with a known melatonin imbalance. In Europe, for instance, melatonin is increasingly prescribed for children with autism and ADHD [28, 29].
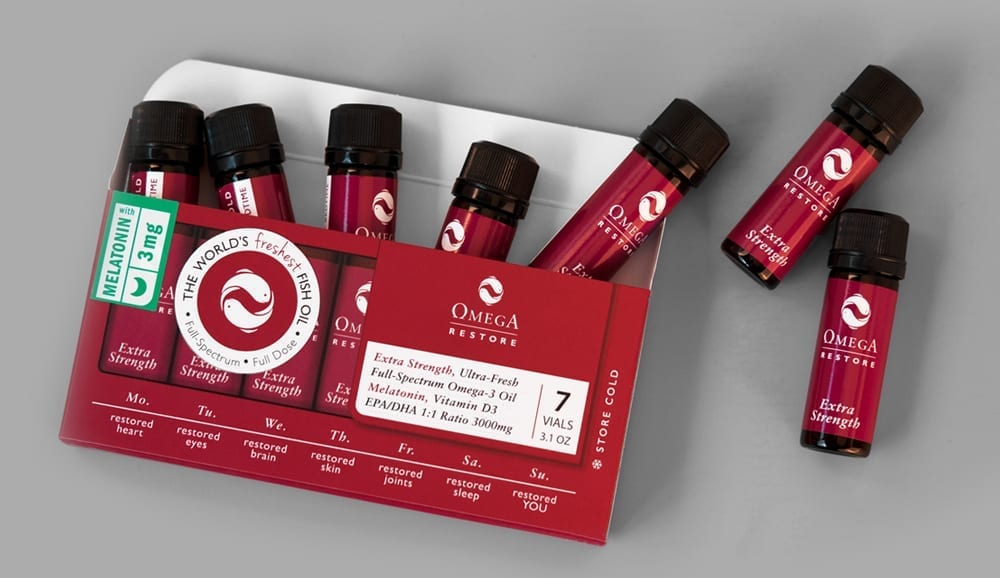
Melatonin and more: Each vial of Omega Restore contains 3000 mg of EPA/DHA omega-3s, 1400 IUs of vitamin D3, and a choice of either 2, 3, 5, or 9 mg of melatonin.
For healthy individuals who already have a solid production of melatonin, taking supplemental melatonin isn’t usually necessary. And for some demographics (like pregnant women), there simply isn’t enough data about melatonin’s effects to provide a recommendation.
You can read more about melatonin’s safety profile here, as well as how to find the right melatonin dose for you here.
Omega Restore: The Perfect Combination of Fish Oil and Melatonin
As you can see, infusing melatonin into our high-quality fish oil is about more than sleep. The dynamic interaction of these amazing compounds is a game-changer for all of us concerned about inflammation and oxidative stress.
With our extensive research – and over 15 years in the omega-3 industry – our physician-led team is proud to produce Omega Restore. It’s the only product on the market that harnesses the power of fresh omega-3s, vitamin D and melatonin, all in one supplement.
Whether or not you nap like a log, Omega Restore may be the night cap of your wellness dreams.
For More Restful Sleep and Energy
Experience the Omega3 Innovations difference for yourself with the most effective fish oil supplement on the market.
Buy Now
References:
1. Manchester, L. C. et al. (2015). Melatonin: An Ancient Molecule that Makes Oxygen Metabolically Tolerable. Journal of Pineal Research, 59, 403-419.
2. Montilla-López, P. et al. (2002). Comparison of Melatonin Versus Vitamin C on Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Enzyme Activity in Alzheimer’s Disease Induced by Okadaic Acid in Neuroblastoma Cells. European Journal of Pharmacology, 451(3), 237-43.
3. Montilla, P., Cruz, A., Padillo, F. J., Túnez, I., Gascon, F., Muñoz, M. C. , Gómez, M., & Pera, C. (2001). Melatonin Versus Vitamin E as Protective Treatment Against Oxidative Stress After Extra-hepatic Bile Duct Ligation in Rats. Journal of Pineal Research, 31(2), 138-44.
4. Leaden, P., Barrionuevo, J., & Catalá, A. (2002). The Protection of Long Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids by Melatonin During Nonenzymatic Lipid Peroxidation of Rat Liver Microsomes. Journal of Pineal Research, 32(3), 129-34.
5. Rosales-Corral, S. A. et al. (2012). Alterations in Lipid Levels of Mitochondrial Membranes Induced by Amyloid-ß: A Protective Role of Melatonin. International Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
6. Nelson, J. R. & Raskin, S. (2019). The Eicosapentaenoic Acid: Arachidonic Acid Ratio and Its Clinical Utility in Cardiovascular Disease. Postgraduate Medical Journal, 131(4), 268-277.
7. Nagata, M., Hata, J. et al. (2017). The Ratio of Serum Eicosapentaenoic Acid to Arachidonic Acid and Risk of Cancer Death in a Japanese Community: The Hisayama Study. Journal of Epidemiology, 27(12), 578–583.
8. Catalá, A. (2010). The Function of Very Long Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in the Pineal Gland. Biochimica Biophysica Acta, 1801(2), 95-9.
9. Lavialle, M., Champeil-Potokar, G. et al. (2008). An (n-3) Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid-Deficient Diet Disturbs Daily Locomotor Activity, Melatonin Rhythm, and Striatal Dopamine in Syrian Hamsters. Journal of Nutrition, 138(9), 1719-24.
10. Ying Dai, Jianghong Liu. (2021). Omega-3 Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid and Sleep: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials and Longitudinal Studies. Nutrition Reviews, 79(8), 847–868.
11. Patan, M. J., Kennedy, D. O. et al. (2021). Differential Effects of DHA- and EPA-Rich Oils on Sleep in Healthy Young Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 13(1).
12. Calder, P. C. (2017). Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Inflammatory Processes: From Molecules to Man. Biochemical Society Transactions, 45(5), 1105-1115.
13. Ferlazzo, N., Andolina, G., Cannata, A., Costanzo, M. G., Rizzo, V., Currò, M., Lentile, R., & Caccamo, D. (2020). Is Melatonin the Cornucopia of the 21st Century?. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland), 9(11).
14. Hardeland, R. (2018). Melatonin and Inflammation-Story of a Double-Edged Blade. Journal of Pineal Research, 65(4).
15. DiNicolantonio, J. J. & O’Keefe, J. H. (2020). The Importance of Marine Omega-3s for Brain Development and the Prevention and Treatment of Behavior, Mood, and Other Brain Disorders. Nutrients, 12(8), 2333.
16. Gow, R. V. & Hibbeln, J. R. (2014). Omega-3 Fatty Acid and Nutrient Deficits in Adverse Neurodevelopment and Childhood Behaviors. Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 23(3), 555–590.
17. Reiter, R. J., Rosales-Corral, S. A., Tan, D. X., Acuna-Castroviejo, D., Qin, L., Yang, S. F., & Xu, K. (2017). Melatonin, a Full Service Anti-Cancer Agent: Inhibition of Initiation, Progression and Metastasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(4):843.
18. Li, Y., Li, S., Zhou, Y., Meng, X., Zhang, J. J., Xu, D. P., & Li, H. B. (2017). Melatonin for the Prevention and Treatment of Cancer. Oncotarget, 8(24), 39896–39921.
19. Menéndez-Menéndez, J. & Martínez-Campa, C. (2018). Melatonin: An Anti-Tumor Agent in Hormone-Dependent Cancers. International Journal of Endocrinology, 2018, 3271948.
20. West, L. et al. (2020). Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA), an Omega-3 Fatty Acid, Inhibits Tumor Growth and Metastatic Potential of Ovarian Cancer. American Journal of Cancer Research, 10(12), 4450–4463.
21. Freitas, R. & Campos, M. M. (2019). Protective Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Cancer-Related Complications. Nutrients, 11(5), 945.
22. Cardinali, D. P. (2019). Melatonin: Clinical Perspectives in Neuro-degeneration. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 10, 480.
23. Sinclair, A. J. (2019). Docosahexaenoic Acid and the Brain – What Is Its Role? Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 28(4), 675-688.
24. Martínez-Águila, A., Martín-Gil, A., Carpena-Torres, C., Pastrana, C., & Carracedo, G. (2021). Influence of Circadian Rhythm in the Eye: Significance of Melatonin in Glaucoma. Biomolecules, 11(3), 340.
25. Calder, P. C. (2018). Very Long-Chain n-3 Fatty Acids and Human Health: Fact, Fiction, and the Future. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society, 77(1), 52-72.
26. Downie, L. E., Ng, S. M., Lindsley, K. B., & Akpek, E. K. (2019). Omega-3 and Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids for Dry Eye Disease. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 12(12).
27. Wu, Y. H. & Swaab, D. F. (2005). The Human Pineal Gland and Melatonin in Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease. Journal of Pineal Research, 38, 145-152.
28. Rzepka-Migut, B., & Paprocka, J. (2020). Efficacy and Safety of Melatonin Treatment in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder-A Review of the Literature. Brain Sciences, 10(4), 219.
29. Parvataneni, T., Srinivas, S., Shah, K., & Patel, R. S. (2020). Perspective on Melatonin Use for Sleep Problems in Autism and Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Trials. Cureus, 12(5).
Popular posts


Related posts